Difference between revisions of "Neural aesthetics"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search

(→2020) |
|||
| (9 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 74: | Line 74: | ||
* [https://mak.at/aisymposium AI Symposium: Uncanny Values], MAK – Museum of Applied Arts, Vienna, 24 Sep 2019. | * [https://mak.at/aisymposium AI Symposium: Uncanny Values], MAK – Museum of Applied Arts, Vienna, 24 Sep 2019. | ||
* [https://www.cais.nrw/veranstaltungen/what-is-the-art-in-artificial-intelligence/ SUSI.ai: What is the Art in Artificial Intelligence?], workshop, Center for Advanced Internet Studies (CAIS), Bochum, 14-15 Nov 2019. Organised by [[Renée Ridgway]]. | * [https://www.cais.nrw/veranstaltungen/what-is-the-art-in-artificial-intelligence/ SUSI.ai: What is the Art in Artificial Intelligence?], workshop, Center for Advanced Internet Studies (CAIS), Bochum, 14-15 Nov 2019. Organised by [[Renée Ridgway]]. | ||
| + | * [https://www.sciarc.edu/events/events/fear-and-wonder-3 Fear and Wonder 3: Futures of AI Symposium], W.M. Keck Lecture Hall, Los Angeles, 20 Nov 2019. Curated by Liam Young. [https://www.facebook.com/events/1194517450752589/] | ||
* [http://electromuseum.ru/en/event/learning-machines-obuchennye-mashiny/ Learning Machines], exhibition, Electromuseum, Moscow, 13 Dec 2019-2 Feb 2020. Curated by Helena Nikonole and [[Alexei Shulgin]]. | * [http://electromuseum.ru/en/event/learning-machines-obuchennye-mashiny/ Learning Machines], exhibition, Electromuseum, Moscow, 13 Dec 2019-2 Feb 2020. Curated by Helena Nikonole and [[Alexei Shulgin]]. | ||
* [https://neurips2019creativity.github.io/ Machine Learning for Creativity and Design: NeurIPS 2019 Workshop], Vancouver, 14 Dec 2019. [http://www.aiartonline.com/ AI Art Gallery], compiled from art, music and design submissions. | * [https://neurips2019creativity.github.io/ Machine Learning for Creativity and Design: NeurIPS 2019 Workshop], Vancouver, 14 Dec 2019. [http://www.aiartonline.com/ AI Art Gallery], compiled from art, music and design submissions. | ||
| Line 81: | Line 82: | ||
* [https://kunsthalltrondheim.no/utstillinger/jenna-sutela/?lang=en Jenna Sutela: NO NO NSE NSE], exhibition, Kunsthall Trondheim, Trondheim, 4 Mar-3 May 2020. Curated by Stefanie Hessler. | * [https://kunsthalltrondheim.no/utstillinger/jenna-sutela/?lang=en Jenna Sutela: NO NO NSE NSE], exhibition, Kunsthall Trondheim, Trondheim, 4 Mar-3 May 2020. Curated by Stefanie Hessler. | ||
* [https://zkm.de/en/exhibition/2020/03/artificial-empathy-installationen Artificial Empathy – Installationen], exhibition, ZKM, Karlsruhe, 27-29 Mar 2020. Accompanied the [https://zkm.de/en/event/2020/03/artificial-empathy Artificial Empathy: International Conference on Artificial Emotions and Affective Computing]. | * [https://zkm.de/en/exhibition/2020/03/artificial-empathy-installationen Artificial Empathy – Installationen], exhibition, ZKM, Karlsruhe, 27-29 Mar 2020. Accompanied the [https://zkm.de/en/event/2020/03/artificial-empathy Artificial Empathy: International Conference on Artificial Emotions and Affective Computing]. | ||
| + | * [https://www.ainarratives.com/jewishai ‘An Epoch of Golem-Making’: Artificial Intelligence and the Jewish Imaginary], workshop, 12 Nov 2020. Organised by the Leverhulme Centre for the Future of Intelligence (University of Cambridge) and Periculum (Charles University) as part of the [https://www.ainarratives.com Global AI Narratives Project]. | ||
| + | * [http://www.nabi.or.kr/en/page/board_view.php?brd_idx=1084&brd_id=project Art, AI and Everything Else], online conference, Art Center Nabi, 3-5 Dec 2020. Organised by Art Center Nabi and the Research Unit for Public Cultures and the Communicative Cities Stream in the Center of Visual Arts, University of Melbourne. | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| Line 137: | Line 140: | ||
* [http://www.aiartonline.com/ AI Art Gallery], a collection of art, music and design using machine learning, since 2017. Curated by Luba Elliott. | * [http://www.aiartonline.com/ AI Art Gallery], a collection of art, music and design using machine learning, since 2017. Curated by Luba Elliott. | ||
* [https://blog.mozilla.org/blog/2018/06/04/mozilla-announces-225000-for-art-and-advocacy-exploring-artificial-intelligence/ Mozilla Award for Art and Advocacy Exploring Artificial Intelligence], 2018. | * [https://blog.mozilla.org/blog/2018/06/04/mozilla-announces-225000-for-art-and-advocacy-exploring-artificial-intelligence/ Mozilla Award for Art and Advocacy Exploring Artificial Intelligence], 2018. | ||
| + | * [https://www.ainarratives.com Global AI Narratives Project], Leverhulme Centre for the Future of Intelligence (University of Cambridge), since 2018. | ||
==Literature, data, resources== | ==Literature, data, resources== | ||
| Line 187: | Line 191: | ||
* Joanna Zylinska, ''[http://www.openhumanitiespress.org/books/titles/ai-art/ AI Art: Machine Visions and Warped Dreams]'', Open Humanities Press, Jul 2020, 176 pp, [[Media:Zylinska_Joanna_AI Art Machine Visions and Warped Dreams 2020.pdf|PDF]]. | * Joanna Zylinska, ''[http://www.openhumanitiespress.org/books/titles/ai-art/ AI Art: Machine Visions and Warped Dreams]'', Open Humanities Press, Jul 2020, 176 pp, [[Media:Zylinska_Joanna_AI Art Machine Visions and Warped Dreams 2020.pdf|PDF]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | * [https://www.goethe.de/prj/jad/sk/the/ari.html ''Jádu'': "Cogito ergo robot"], Bratislava: Goethe-Institut, Nov 2020. Special magazine issue. {{sk}},{{cz}}/{{de}} | ||
* ''Art and Machine Learning'', Graz: mur.at, forthcoming. [https://mur.at/post/ml-call-for-papers/ CfP]. [https://mur.at/project/im-netz-der-sinne/] | * ''Art and Machine Learning'', Graz: mur.at, forthcoming. [https://mur.at/post/ml-call-for-papers/ CfP]. [https://mur.at/project/im-netz-der-sinne/] | ||
| Line 245: | Line 251: | ||
* Nick Dyer-Witheford, Atle Mikkola Kjosen, James Steinhoff, ''[http://library.memoryoftheworld.org/#/book/bd54927b-b27f-4921-9a1a-ecfd6093d748 Inhuman Power: Artificial Intelligence and the Future of Capitalism]'', Pluto Press, Jun 2019. [https://www.plutobooks.com/9780745338606/inhuman-power/ Publisher]. | * Nick Dyer-Witheford, Atle Mikkola Kjosen, James Steinhoff, ''[http://library.memoryoftheworld.org/#/book/bd54927b-b27f-4921-9a1a-ecfd6093d748 Inhuman Power: Artificial Intelligence and the Future of Capitalism]'', Pluto Press, Jun 2019. [https://www.plutobooks.com/9780745338606/inhuman-power/ Publisher]. | ||
| − | * Louise Amoore, [http://sci-hub. | + | * Louise Amoore, [http://sci-hub.se/10.1177/0263276419851846 "Doubt and the Algorithm: On the Partial Accounts of Machine Learning"], ''Theory, Culture & Society'', 26 Jun 2019. |
* Emma Strubell, Ananya Ganesh, Andrew McCallum, [https://arxiv.org/abs/1906.02243 "Energy and Policy Considerations for Deep Learning in NLP"], in ''57th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (ACL)'', Jul 2019. [https://www.technologyreview.com/s/613630/training-a-single-ai-model-can-emit-as-much-carbon-as-five-cars-in-their-lifetimes/ Summary]. | * Emma Strubell, Ananya Ganesh, Andrew McCallum, [https://arxiv.org/abs/1906.02243 "Energy and Policy Considerations for Deep Learning in NLP"], in ''57th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (ACL)'', Jul 2019. [https://www.technologyreview.com/s/613630/training-a-single-ai-model-can-emit-as-much-carbon-as-five-cars-in-their-lifetimes/ Summary]. | ||
| Line 263: | Line 269: | ||
* Krystian Woznicki, [https://blogs.mediapart.fr/krystian-woznicki/blog/270120/silent-works-what-hidden-human-labor-ai-driven-capitalism "Silent Works: What Is the Hidden Human Labor In AI-Driven Capitalism?"], ''Mediapart'', 27 Jan 2020. [https://projekte.berlinergazette.de/silent-works/ Project website]. | * Krystian Woznicki, [https://blogs.mediapart.fr/krystian-woznicki/blog/270120/silent-works-what-hidden-human-labor-ai-driven-capitalism "Silent Works: What Is the Hidden Human Labor In AI-Driven Capitalism?"], ''Mediapart'', 27 Jan 2020. [https://projekte.berlinergazette.de/silent-works/ Project website]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Mark Coeckelbergh, ''[https://aaaaarg.fail/thing/5e7517579ff37c6aef2e81c3 AI Ethics]'', MIT Press, Apr 2020, 248 pp. [https://mitpress.mit.edu/books/ai-ethics] | ||
* Vladan Joler, Matteo Pasquinelli, [https://monoskop.org/log/?p=22167 "The Nooscope Manifested: AI as Instrument of Knowledge Extractivism"], Karlsruhe: KIM research group (Karlsruhe University of Arts and Design), and Novi Sad: Share Lab, 1 May 2020. | * Vladan Joler, Matteo Pasquinelli, [https://monoskop.org/log/?p=22167 "The Nooscope Manifested: AI as Instrument of Knowledge Extractivism"], Karlsruhe: KIM research group (Karlsruhe University of Arts and Design), and Novi Sad: Share Lab, 1 May 2020. | ||
| Line 269: | Line 277: | ||
* Michael J. Lyons, [https://arxiv.org/abs/2009.01215 "Excavating "Excavating AI": The Elephant in the Gallery"], ''arXiv.org'', Sep 2020. | * Michael J. Lyons, [https://arxiv.org/abs/2009.01215 "Excavating "Excavating AI": The Elephant in the Gallery"], ''arXiv.org'', Sep 2020. | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Tomasz Hollanek, [https://doi.org/10.1007/s00146-020-01110-y "AI Transparency: A Matter of Reconciling Design with Critique"], ''AI & Society'', Nov 2020. | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Yarden Katz, ''Artificial Whiteness: Politics and Ideology in Artificial Intelligence'', Columbia University Press, Nov 2020, 352 pp. [https://cup.columbia.edu/book/artificial-whiteness/9780231194914] | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Kate Crawford, ''Atlas of AI: Power, Politics, and the Planetary Costs of Artificial Intelligence'', Yale University Press, forthcoming 2021. [https://yalebooks.yale.edu/book/9780300209570/atlas-ai] | ||
; more | ; more | ||
| Line 338: | Line 352: | ||
* Jürgen Schmidhuber, [http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0893608014002135 "Deep Learning in Neural Networks: An Overview"], ''ScienceDirect'' 61, Jan 2015, pp 85-117. [http://www.idsia.ch/~juergen/deep-learning-overview.html] | * Jürgen Schmidhuber, [http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0893608014002135 "Deep Learning in Neural Networks: An Overview"], ''ScienceDirect'' 61, Jan 2015, pp 85-117. [http://www.idsia.ch/~juergen/deep-learning-overview.html] | ||
| − | * Yann LeCun, Yoshua Bengio, Geoffrey Hinton, [http://sci-hub. | + | * Yann LeCun, Yoshua Bengio, Geoffrey Hinton, [http://sci-hub.se/10.1038/nature14539 "Deep Learning"], ''Nature'' 521, 28 May 2015, pp 436-444. Critiqued by [http://people.idsia.ch/~juergen/deep-learning-conspiracy.html Schmidhuber] recasting the recent advances of deep learning as building on top of prior work with multilayer neural networks, going back decades. |
* Andrey Kurenkov, [http://www.andreykurenkov.com/writing/a-brief-history-of-neural-nets-and-deep-learning/ "A 'Brief' History of Neural Nets and Deep Learning"], [http://www.andreykurenkov.com/writing/a-brief-history-of-neural-nets-and-deep-learning-part-2 Part 2], [http://www.andreykurenkov.com/writing/a-brief-history-of-neural-nets-and-deep-learning-part-3/ Part 3], [http://www.andreykurenkov.com/writing/a-brief-history-of-neural-nets-and-deep-learning-part-4 Part 4], ''Andrey Kurenkov'' blog, 24 Dec 2015. | * Andrey Kurenkov, [http://www.andreykurenkov.com/writing/a-brief-history-of-neural-nets-and-deep-learning/ "A 'Brief' History of Neural Nets and Deep Learning"], [http://www.andreykurenkov.com/writing/a-brief-history-of-neural-nets-and-deep-learning-part-2 Part 2], [http://www.andreykurenkov.com/writing/a-brief-history-of-neural-nets-and-deep-learning-part-3/ Part 3], [http://www.andreykurenkov.com/writing/a-brief-history-of-neural-nets-and-deep-learning-part-4 Part 4], ''Andrey Kurenkov'' blog, 24 Dec 2015. | ||
* Stephanie Dick, [https://hdsr.mitpress.mit.edu/pub/0aytgrau "Artificial Intelligence"], ''Harvard Data Science Review'' 1, 23 Jun 2019. | * Stephanie Dick, [https://hdsr.mitpress.mit.edu/pub/0aytgrau "Artificial Intelligence"], ''Harvard Data Science Review'' 1, 23 Jun 2019. | ||
Revision as of 17:18, 5 December 2020

Partial results of the "hello world" test of a machine learning algorithm, automated recognition of handwritten digits, showing 125 test cases that the network got wrong. Each case is labeled by the network’s guess. The true classes are arranged in standard scan order. Source: Hinton et al 2006.

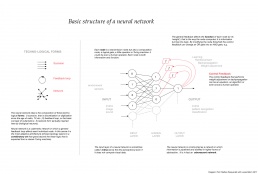
Basic structure of a neural network. Several techno-logical forms can be identified in the concept: scansion, that is discretisation or digitisation since the age of radio, TV, etc.; feedback loop, or the basic concept of cybernetics; and network form, here inspired by biological neurons. Diagram by Matteo Pasquinelli with Lukas Rehm, 2017. Source.
A resource on recent work between art/design and artificial neural networks in machine learning.
Related notions: AI art, creative AI, art and artificial intelligence.
Contents
- 1 Events
- 2 Artists, designers, writers, musicians, makers
- 3 Initiatives
- 4 Literature, data, resources
- 4.1 Arts practice and criticism
- 4.2 Online galleries and collections
- 4.3 Recent debates on artificial intelligence in the humanities and social sciences
- 4.4 Software
- 4.5 Datasets
- 4.6 Courses and textbooks for artists
- 4.7 Research papers
- 4.8 Scientific introduction into deep learning
- 4.9 Historization of deep learning
Events
2014
- Olivier Alary & Gregory Chatonsky: Capture, I'll Be Your Mirror, exhibition, Arts Center, Enghein-les-Bains, 10 Apr-6 Jul 2014. [1]. Capture is a generative rockband. Some examples of MIDI music generated by recursive neural network.
2015
- The Lab at the Google Cultural Institute, Paris, launches a 'machine learning for art' residency, early 2015 - mid-2016. Artists: Mario Klingemann, Cyril Diagne. Talk. Works.
- DeepDream launched by Google's software engineers Alexander Mordvintsev, Christopher Olah and Mike Tyka, 17 Jun 2015. Reddit post from a day earlier. Vice coverage. Source code.
- (Artifical Intelligence) Digitale Demenz exhibition, HMKV, Dortmund, 14 Nov 2015-6 Mar 2016. An exhibition exploring the relationship between contemporary art and artificial intelligence. Works by Erik Bünger, John Cale, Brendan Howell, Chris Marker, Julien Prévieux, Suzanne Treister, and !Mediengruppe Bitnik. Curated by Thibaut de Ruyter.
2016
- DeepDream: The Art of Neural Networks, 26-27 Feb 2016. Exhibition and symposium. Organised by Gray Area Foundation for the Arts and Research at Google.
- alt-AI: exploring the intersection of artificial intelligence and art, School for Poetic Computation, New York, 20-22 May 2016. Symposium and exhibition. Video recordings of talks: Gene Kogan, Golan Levin, Cassie Tarakajian, Hannah Davis, Rebecca Fiebrink, Mike Tyka, Heather Dewey-Hagborg, Brian Whitman, Allison Parrish, Mario Klingemann, Lynn Cherny, Kathryn Hume; performance: Jason Levine. Interviews (15 min), Exhibition highlights (2 min). Website mirror.
- Music, Art & Machine Intelligence workshop, San Francisco, 1 Jun 2016. Jointly hosted by Google's AMI and Magenta groups. Video recordings of talks. Proceedings.
- Recognition exhibition, Tate Britain, London, 2 Sep-27 Nov 2016. An artificial intelligence program that compared artworks with up-to-the-minute photojournalism. Developed by Jolibrain (Alexandre Girard and Emmanuel Benazera) and Fabrica. More.
- Neuronal Creation, exhibition and discussion track at Retune Festival, Berlin, 6-8 Oct 2016. Report: Elliott (Medium).
- Machine Research – Research/PhD Workshop 2016, Brussels, 24-26 Oct 2016. Organised by Aarhus University, transmediale, and Constant. Contributes to the transmediale festival programme for 2017.
- STATE Festival 2016, Kühlhaus, Berlin, 4-5 Nov 2016. Conference, exhibition, performances, screenings and workshops exploring the intersection of current emotions research and artificial intelligence. Director: Christian Rauch.
- How Deep is Your Dream, Merz Akademie, Stuttgart, 8 Nov - 6 Dec 2016. Weekly lecture series curated and moderated by Olia Lialina. Video recordings of talks: Sebastian Schmieg, Frieder Nake, Gene Kogan, Simone C. Niquille.
2017
- Machine Fictions exhibition, part of Leverhulme Centre for the Future of Intelligence Annual Conference, Webb Library, Jesus College, Cambridge, UK, 13-14 Jul 2017. Curated by Luba Elliott.
- An AI Summer web residency programme, Akademie Schloss Solitude, Stuttgart, Summer 2017. Curated by Nora O Murchú. In collaboration with ZKM.
- Ars Electronica: AI. Artificial Intelligence. Das andere Ich / The Other I, Linz, 7-11 Sep 2017. Festival featuring exhibitions, performances, conferences, etc. Catalogue.
- The Age of AI Artisans, State of AI Pop-Up Studio, Los Angeles, 3-29 Oct 2017. Exhibition featuring Unhuman: Art in the Age of AI, the first exhibition on art produced by the AICAN Algorithm.
- Facets: Un-Conference on Art & Artificial Intelligence, Goethe Institut, New York, 28 Oct 2017. Video recordings. Report: Bishop (LIS Theory).
- First Workshop on the History of Expressive Systems, part of the International Conference on Interactive Digital Storytelling (ICIDS), Funchal, Madeira, Portugal, 14 Nov 2017.
- ASYNC: Asynchronous Research on AI & Games, MetaMakers Institute, Falmouth University, Falmouth, UK, 25-27 Oct 2017. Incl. video recordings.
2018
- When the Machine Makes Art, a special edition of Creative Coding Utrecht (CCU), De Stadstuin, Utrecht, 14 Jan 2018.
- I.A.rt Colloquium: Artificial Intelligence and Data Serving Creative Work for Public Spaces, Pavillon Sherbrooke, Université du Québec à Montréal, Montreal, 22 Feb 2018. Programme.
- Ars Incognita: Poetics of Artificial Creativity: Symposium on Art and Artificial Intelligence, Centro Atlántico de Arte Moderno (CAAM), Spain, 15-17 Mar 2018. Dir. Héctor Rodríguez, associate dir. Tomás Laurenzo, artistic dir. Álvaro Rodríguez Fominaya.
- Encoding Cultures: Living Amongst Intelligent Machines conference, ZKM, Karlsruhe, 27-28 Apr 2018. Video recordings.
- Art-AI Festival, Phoenix Arts Centre & Highcross Leicester, Leicester, UK, 30 Apr-13 May 2018.
- Politics of Machines – Art and After, 1st Electronic Visualisation & the Arts (EVA) conference, Aalborg University, Copenhagen, 15-17 May 2018. Chaired by Laura Beloff and Morten Søndergaard. Organised by Aalborg University (Aalborg, Copenhagen) and Dias: Digital Interactive Art Space (Copenhagen).
- Im Netz der Sinne workshop, Kultur in Graz, Graz, 24-26 May 2018. Organised by mur.at.
- Machine Dreams exhibition, part of CogX 2018 conference, Tobacco Dock, London, 11-12 Jun 2018. Curated by Luba Elliott; commissioned by Tabitha Goldstaub. Artist interviews (Forbes).
- Art Assembly: Machine Learning, Fiber, Amsterdam, 22 Jun 2018. Organised by Fiber as part of the Coded Matter(s): Worldbuilding series.
- Christie's auctions work made by the French collective Obvious, first announced Aug 2018, sold for $432,500 on 25 Oct 2018; sparking debate from established artists in the field, 25 Sep 2018; and prompting further investigation, 14 Oct 2018.
- Seoul Mediacity Biennale 2018: Eu Zen exhibition, Seoul Museum of Art, Seoul, 6 Sep-18 Nov 2018.
- Artificially Intelligent, exhibition, part of Digital Design Weekend, V&A, London, 6 Sep-31 Dec 2018. Booklet. Summary.
- First Workshop on Computer Vision for Fashion, Art and Design, part of European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, 14 Sep 2018. Selected artworks.
- LuxLogAI 2018: Luxembourg Logic for AI Summit: AI + Art, University of Luxembourg, Luxembourg, 17-21 Sep 2018. Organised by Yolanda Spinola-Elias and Egberdien van der Torre.
- Artificial Intelligence / Intelligent Art: Student Conference on Art, Copenhagen University, Copenhagen, 1-2 Oct 2018.
- Pierre Huyghe: UUmwelt exhibition, Serpentine Galleries, London, 3 Oct 2018-10 Feb 2019. Exhibition guide. Interview (Guardian).
- Paradox: The Body in the Age of AI, exhibition, Miller Institute for Contemporary Art/Carnegie Mellon University, Pittsburgh, 5 Oct 2018-3 Feb 2019. Curated by Elizabeth Chodos.
- E-relevance of Culture in the Age of AI, expert seminar, Rijeka, Croatia, 12-13 Oct 2018. Organised in the framework of the Croatian Chairmanship of the Committee of Ministers of the Council of Europe. Video testimonials.
- Art and AI: Shamans of the Digital Renaissance, salon and performances, Silent Green, Berlin, 18 Oct 2018.
- Ambient Revolts: How Can We Rethink Political Agency in an AI-Driven World, Berliner Gazette Annual Conference 2018, ZK/U – Center for Arts and Urbanistics, Berlin, 8-10 Nov 2018. Incl. video recordings.
- Post-Binary: A Conference on Artificial Intelligence in Art and Design, Museum Angewandte Kunst, Frankfurt am Main, 10 Nov 2018.
- sensu lato :: im weiteren Sinne exhibition, Akademie Graz, Graz, 24 Nov-14 Dec 2018. Organised by mur.at.
- Machine Learning for Creativity and Design, NIPS 2018 Workshop, Montreal, 8 Dec 2018. Organised by Luba Elliott, Sander Dieleman, Rebecca Fiebrink, Adam Roberts, Jesse Engel, and Tom White.
2019
- Art Machines: International Symposium on Computational Media Art (ISCMA) 2019, School of Creative Media, City University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong, 4-7 Jan 2019. Dir. Richard Allen, co-directors (machine learning and art): Hector Rodriguez, Tomas Laurenzo.
- Neural Plasticity, exhibition, On Canal, New York, 6-23 Mar 2019. Curated by Julia Kaganskiy for The Current Museum. [2]
- Vertiginous Data exhibition, National Museum of Modern and Contemporary Art Korea, Seoul, 23 Mar-28 Jul 2019.
- Data Workers, exhibition, Mundaneum, Mons (Belgium), 28 Mar-29 Apr 2019. Created by members of Algolit.
- Datatata conference, Faculty of Fine Arts at Brno University of Technology, Brno, 12 Apr 2019.
- Another AI in Art: Decolonizing Artificial Intelligence (AI) and the Future of Art Making, summit, New Museum, New York, 24-27 Apr 2019.
- Entangled Realities – Living with Artificial Intelligence Entangled Realities. Living with Artificial Intelligence, exhibition, HEK - House of Electronic Arts, Basel, 9 May-11 Aug 2019. Curated by Sabine Himmelsbach and Boris Magrini.
- AI x Art Symposium, New York Live Arts Theater, New York, 11 May 2019.
- AI: More than Human exhibition, Barbican, London, 16 May-26 Aug 2019. Review: Jones (Guardian).
- Uncanny Values: Artificial Intelligence & You exhibition, MAK, Vienna, 29 May-6 Oct 2019. Curated by Paul Feigelfeld and Marlies Wirth. [3]
- Re-imagining AI: Scholars, Artists and Designers in Dialogue, symposium, Institute of Experimental Design and Media Cultures IXDM, FHNW Academy of Art and Design, Basel, 20-21 Jun 2019. Video documentation.
- Gregory Chatonsky: Terre seconde (Second Earth), exhibition, Palais de Tokyo, Paris, 21 Jun-14 Jul 2019. Curated by Gael Charbau. [4]
- Higher Resolution with Hyphen-Labs, workshop, Tate Modern, London, 17-29 Sep 2019.
- AI Symposium: Uncanny Values, MAK – Museum of Applied Arts, Vienna, 24 Sep 2019.
- SUSI.ai: What is the Art in Artificial Intelligence?, workshop, Center for Advanced Internet Studies (CAIS), Bochum, 14-15 Nov 2019. Organised by Renée Ridgway.
- Fear and Wonder 3: Futures of AI Symposium, W.M. Keck Lecture Hall, Los Angeles, 20 Nov 2019. Curated by Liam Young. [5]
- Learning Machines, exhibition, Electromuseum, Moscow, 13 Dec 2019-2 Feb 2020. Curated by Helena Nikonole and Alexei Shulgin.
- Machine Learning for Creativity and Design: NeurIPS 2019 Workshop, Vancouver, 14 Dec 2019. AI Art Gallery, compiled from art, music and design submissions.
2020
- Artificial intelligence at the intersection of art, knowledge and industry, forum, Montreal, 7 Feb 2020. Organised by the Conseil québécois des arts médiatiques in collaboration with Element AI and Hexagram.
- Jenna Sutela: NO NO NSE NSE, exhibition, Kunsthall Trondheim, Trondheim, 4 Mar-3 May 2020. Curated by Stefanie Hessler.
- Artificial Empathy – Installationen, exhibition, ZKM, Karlsruhe, 27-29 Mar 2020. Accompanied the Artificial Empathy: International Conference on Artificial Emotions and Affective Computing.
- ‘An Epoch of Golem-Making’: Artificial Intelligence and the Jewish Imaginary, workshop, 12 Nov 2020. Organised by the Leverhulme Centre for the Future of Intelligence (University of Cambridge) and Periculum (Charles University) as part of the Global AI Narratives Project.
- Art, AI and Everything Else, online conference, Art Center Nabi, 3-5 Dec 2020. Organised by Art Center Nabi and the Research Unit for Public Cultures and the Communicative Cities Stream in the Center of Visual Arts, University of Melbourne.
Artists, designers, writers, musicians, makers
- Memo Akten, @memotv, Istanbul.
- Albert Barqué-Duran, @albertbarque, London, Berlin & Barcelona.
- Algolit, Brussels.
- Robbie Barrat, @DrBeef_, SF Bay Area.
- Anil Bawa-Cavia, @cavvia, Berlin & London.
- Gregory Chatonsky, @chatonsky, Paris & Montreal.
- Ian Cheng, @eyecheng, NYC.
- Sougwen 愫君 Chung, @sougwen, NYC.
- Sofia Crespo, @soficrespo91, Berlin.
- Ursula Damm, Berlin & Weimar.
- Hannah Davis, @ahandvanish, NYC.
- Heather Dewey-Hagborg, @hdeweyh, Chicago & NYC.
- Rebecca Fiebrink, @rebeccafiebrink, London.
- Ross Goodwin, @rossgoodwin, Los Angeles.
- Lenka Hamosova, @lenkahamosova, Prague.
- Lars TCF Holdhus, @larsholdhus, Berlin.
- Mario Klingemann, @quasimondo, Munich.
- Gene Kogan, @genekogan, Berlin.
- Angie Meitzler, Brooklyn, NY.
- Kyle McDonald, @kcimc, Los Angeles.
- Simone C. Niquille, @s__c__n, Amsterdam.
- Helena Nikonole, Moscow.
- Andreas Refsgaard, @AndreasRef, Copenhagen.
- Tivon Rice, @tivonrice, Seattle & The Hague.
- Anna Ridler, @annaridler, London.
- Helena Sarin, @glagolista.
- Philipp Schmitt, @philippschmitt, NYC.
- Yining Shi, @yining_shi, NYC.
- Shinseungback Kimyonghun (Shin Seung Back & Kim Yong Hun), @ssbkyh, Seoul.
- Caroline Sinders, @carolinesanders, New Orleans/Brooklyn
- Xavier Snelgrove, @wxswxs, Toronto.
- Cassie Tarakajian, @hellothisiscass, Brooklyn, NY.
- Francis Tseng, @frnsys, Brooklyn, NY.
- Michael Tyka, @mtyka, Seattle.
- Cristóbal Valenzuela, @c_valenzuelab, NYC.
- Tom White, @dribnet, Wellington.
- Samim Winiger, @samim, Berlin.
Initiatives
- School for Poetic Computation, founded 2013 in New York. @sfpc.
- School of Machines, Making & Make-Believe, founded March 2014 in Berlin by Rachel Uwa.
- Fast Forward Labs, a machine intelligence research company, New York.
- Artists and Machine Intelligence (AMI). A program at Google that brings together artists and engineers to realize projects using Machine Intelligence. [6]
- Magenta, a Google Brain project dedicated to generating art and music using machine learning. Started in June 2016. [7]
- Art and Artificial Intelligence Laboratory, Rutgers University, New Brunswick, NJ. Founding director: Ahmed Elgammal.
- Creative AI meetup group, since September 2016. Founded by Luba Elliott.
- Feminist.AI, a community AI research and design group focused on critical making as a response to hegemonic AI, est. 2016.
- AI Now Institute, New York University. A research institute examining the social implications of artificial intelligence. Founded in 2017 by Kate Crawford and Meredith Whittaker.
- Artificial imagination / Artificielle postdigital, a research seminar on contemporary art and artificial intelligence, Ecole Normale Superieure, Paris. Founded in 2017 by Béatrice Joyeux-Prunel and Grégory Chatonsky. Twitter.
- AI Art Gallery, a collection of art, music and design using machine learning, since 2017. Curated by Luba Elliott.
- Mozilla Award for Art and Advocacy Exploring Artificial Intelligence, 2018.
- Global AI Narratives Project, Leverhulme Centre for the Future of Intelligence (University of Cambridge), since 2018.
Literature, data, resources
Arts practice and criticism
- Melpomene, Bagabone, Hem ‘I Die Now, New York: Vantage Press, 1980, 136 pp. Perhaps the first novel that was purportedly written by a computer.
- Miguel Carvalhais, Artificial Aesthetics: Creative Practices in Computational Art and Design, forew. Heitor Alvelos and Penousal Machado, Porto: U.Porto Edições, 2016, 307 pp. [8]
- Luba Elliott, "The art side of AI at transmediale + CTM", Medium, 10 Apr 2017.
- Luba Elliott, Creative AI Newsletter, since May 2017.
- Digimag 76: "Smart Machines for Enhanced Arts", eds. Silvia Bertolotti and Marco Mancuso, Milan: Digicult, Summer 2017, 74 pp, EPUB. Texts by Memo Akten, Claire Burke, Geoffrey Drake-Brockman, Jerry Galle, Eugene Kogan, Robert B. Lisek, Filippo Lorenzin, Andreas Refsgaard, Liu Yuxi, Alessandro Masserdotti. [9]
- Ars Electronica: AI. Artificial Intelligence. Das andere Ich / The Other I, eds. Gerfried Stocker, Christine Schöpf and Hannes Leopoldseder, Berlin: Hatje Cantz, 2017, 400 pp. Catalogue. Festival.
- Flash Art 316: "Artificial Intelligence", Sep-Oct 2017, 132 pp. [10] [11]
- Jason Bailey's writing and interviews on Artnome, since Oct 2017.
- Simon Parkin, "AI Is Dreaming Up New Kinds of Video Games", MIT Technology Review, 29 Nov 2017.
- Aaron Hertzmann, "Can Computers Create Art?", Arts 7:2, 10 May 2018.
- Sam Gaskin, "When Art Created by Artificial Intelligence Sells, Who Gets Paid?", Artsy, 17 Sep 2018.
- Ahmed Elgammal, "With AI Art, Process Is More Important Than the Product", Smithsonian.com, 16 Oct 2018.
- Naomi Rea, "Has Artificial Intelligence Brought Us the Next Great Art Movement? Here Are 9 Pioneering Artists Who Are Exploring AI’s Creative Potential", Artnet News, 6 Nov 2018.
- Algolit, Data Workers, Brussels: Constant, Mar 2019. (English)/(French)
- Ian Bogost, "The AI-Art Gold Rush Is Here", The Atlantic, 6 Mar 2019.
- Fabian Offert, "The Past, Present, and Future of AI Art", The Gradient, 18 Jun 2019.
- Shauna Jean Doherty, "Art in the Age of Artificial Intelligence", esse 97: "Appropriation", Autumn 2019, pp 30-41. [12]
- Luke Stark, Kate Crawford, "The Work of Art in the Age of Artificial Intelligence: What Artists Can Teach Us About the Ethics of Data Practice", Surveillance & Society 17(3-4): "Visibilities and New Models of Policing", Sep 2019.
- Entangled Realities: Living with Artificial Intelligence / Leben mit künstlicher Intelligenz, eds. Sabine Himmelsbach and Boris Magrini, Merian, 2019, 229 pp. Catalogue. Exhibition. Review: Cianciotta (Neural). (English)/(German)
- Marco Donnarumma, Wesley Goatley, Helena Nikonole, "Critical Art and the Ethics of AI", Dec 2019ff. [13]
- Espace 124: "IA, art sans artistes? / AI, art without artists?", Montreal, Jan 2020. Special issue of magazine. Introduction. TOC. (French)/(English)
- Yair Rubinstein, "Uneasy Listening: Towards a Hauntology of AI-Generated Music", Resonance 1:1, Spring 2020, pp 77-93.
- Joanna Zylinska, AI Art: Machine Visions and Warped Dreams, Open Humanities Press, Jul 2020, 176 pp, PDF.
- Jádu: "Cogito ergo robot", Bratislava: Goethe-Institut, Nov 2020. Special magazine issue. (Slovak),(Czech)/(German)
Online galleries and collections
See also exhibitions in the Events section above.
- Art Gallery: NIPS Machine Learning for Creativity and Design, a collection of art, music and design using machine learning. A part of the NIPS Machine Learning for Creativity and Design Workshop 2017. Curated by Luba Elliott.
- Computer Vision Art Gallery, 2018. Organised by Xavier Snelgrove and Luba Elliott.
Recent debates on artificial intelligence in the humanities and social sciences
- Nora N. Khan, "Towards a Poetics of Artificial Superintelligence", After Us, 25 Sep 2015.
- Florian Hecker, Robin Mackay, "On Sound and Artificial Neural Networks", in Writing and Unwriting (Media) Art History: Erkki Kurenniemi in 2048, eds. Joasia Krysa and Jussi Parikka, MIT Press, Sep 2015, pp 279-289.
- Matteo Pasquinelli (ed.), Alleys of Your Mind: Augmented Intelligence and Its Traumas, Lüneburg: Meson, Nov 2015, 212 pp.
- Gregory Chatonsky, "Deep Dream (Le rêve du réseau)", Musee d'Art Moderne de la Ville de Paris, Paris, 17 Dec 2015. Lecture given in conjunction with the exhibition Co-Workers. [15] (French)
- A Peer Reviewed Journal About 6(1): "Machine Research", eds. Christian Ulrik Andersen and Geoff Cox, Aarhus: Aarhus University, Apr 2017, 108 pp, PDF. [16]
- Matteo Pasquinelli, "Machines that Morph Logic: Neural Networks and the Distorted Automation of Intelligence as Statistical Inference", Glass Bead 2, Sep 2017. [17]
- Glass Bead 2: "Site 1: Logic Gate, the Politics of the Artifactual Mind", eds. Fabien Giraud, Jeremy Lecomte, Vincent Normand, Ida Soulard, and Inigo Wilkins, Nov 2017. (English)/(French)
- Adrian Mackenzie, Machine Learners: Archaeology of a Data Practice, MIT Press, Nov 2017, 272 pp.
- Eirini Malliaraki, "Toward ethical, transparent and fair AI/ML: a critical reading list", Medium, Feb 2018.
- Agoston Nagy, "Visual Music & Machine Learning Workshop for Kids", Medium, 3 Apr 2018.
- Kate Crawford, Vladan Joler, "Anatomy of an AI System: The Amazon Echo as an Anatomical Map of Human Labor, Data and Planetary Sesources", AI Now Institute/NYU & Share Lab, 7 Sep 2018.
- Clemens Apprich, Wendy Hui Kyong Chun, Florian Cramer, Hito Steyerl, Pattern Discrimination, Lüneburg: meson press, with University of Minnesota Press, Nov 2018, xii+123 pp.
- Jonnie Penn, "AI Thinks Like a Corporation—and That's Worrying", Economist, 26 Nov 2018.
- Report: Montréal Declaration for a Responsible Development of Artificial Intelligence, Montréal, Dec 2018, 305 pp, PDF. (English)
- Montréal Declaration for a Responsible Development of Artificial Intelligence, Montréal, Dec 2018, PDF. (English),(multiple languages)
- Lev Manovich, AI Aesthetics, Moscow: Strelka Press, Dec 2018, 57 pp. Excerpt. [18] [19] [20]
- Hito Steyerl, "The Language of Broken Glass", Berlin: HKW, Jan 2019, 26 min. Lecture-performance video.
- Sarah Myers West, Meredith Whittaker, Kate Crawford, Discriminating Systems: Gender, Race and Power in AI, New York: AI Now Institute, Apr 2019, 33 pp. A report examining the lack of diversity in AI workplaces and biased technologies as deeply interconnected issues. [21]
- Julia Schneider, Lena Kadriye Ziyal, We Need to Talk, AI: A Comic Essay on Artificial Intelligence, Berlin: Julia Schneider, May 2019, 56 pp, EPUB. [22]
- Oscar Williams, "How Big Tech Funds the Debate on AI Ethics", New Statesman, 6 Jun 2019.
- Katerina Cizek, William Uricchio, Sarah Wolozin, "Media Co-Creation with Non-Human Systems", in Cizek, Uricchio, et al., Collective Wisdom: Co-Creating Media within Communities, across Disciplines and with Algorithms, 3 Jun 2019.
- Matteo Pasquinelli, "Three Thousand Years of Algorithmic Rituals: The Emergence of AI from the Computation of Space", e-flux 101, Jun 2019, PDF.
- "算法仪式的三千年史: 人工智能从空间计算的启程", c.2019. [23] (Chinese)
- Nick Dyer-Witheford, Atle Mikkola Kjosen, James Steinhoff, Inhuman Power: Artificial Intelligence and the Future of Capitalism, Pluto Press, Jun 2019. Publisher.
- Louise Amoore, "Doubt and the Algorithm: On the Partial Accounts of Machine Learning", Theory, Culture & Society, 26 Jun 2019.
- Emma Strubell, Ananya Ganesh, Andrew McCallum, "Energy and Policy Considerations for Deep Learning in NLP", in 57th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (ACL), Jul 2019. Summary.
- A Peer-Reviewed Journal About 8(1): "Machine Feeling", eds. Christian Ulrik Andersen and Geoff Cox, Aarhus: Aarhus University, Aug 2019, 219 pp.
- Global Information Society Watch 2019: Artificial Intelligence: Human Rights, Social Justice and Development, Association for Progressive Communications, 2019. Report.
- Kate Crawford, Trevor Paglen, "Excavating AI: The Politics of Images in Machine Learning Training Sets", New York: AI Now Institute, 19 Sep 2019. ImageNet Roulette.
- Spheres 5: "Spectres of AI", Nov 2019.
- Matteo Pasquinelli, "How a Machine Learns and Fails: A Grammar of Error for Artificial Intelligence", PDF.
- AI Now 2019 Report, New York: AI Now Institute, Dec 2019, 100 pp.
- Stephen Cave, Kanta Dihal, Sarah Dillon (eds.), AI Narratives: A History of Imaginative Thinking about Intelligent Machines, Oxford University Press, 2020, 448 pp. [24]
- Krystian Woznicki, "Silent Works: What Is the Hidden Human Labor In AI-Driven Capitalism?", Mediapart, 27 Jan 2020. Project website.
- Vladan Joler, Matteo Pasquinelli, "The Nooscope Manifested: AI as Instrument of Knowledge Extractivism", Karlsruhe: KIM research group (Karlsruhe University of Arts and Design), and Novi Sad: Share Lab, 1 May 2020.
- Gabriele de Seta, "China.ai", in Realtime: Making Digital China, eds. Clément Renaud, Florence Graezer Bideau, and Marc Laperrouza, PURR, 2020, pp 154-169. [26]
- Michael J. Lyons, "Excavating "Excavating AI": The Elephant in the Gallery", arXiv.org, Sep 2020.
- Tomasz Hollanek, "AI Transparency: A Matter of Reconciling Design with Critique", AI & Society, Nov 2020.
- Yarden Katz, Artificial Whiteness: Politics and Ideology in Artificial Intelligence, Columbia University Press, Nov 2020, 352 pp. [27]
- Kate Crawford, Atlas of AI: Power, Politics, and the Planetary Costs of Artificial Intelligence, Yale University Press, forthcoming 2021. [28]
- more
Software
- Tensorflow, an open source machine learning framework. Developed by the Google Brain team for internal Google use. Released under an open-source license on Nov 2015.
- ml5.js, an open source machine learning library for the web. Launched Jun 2018.
- Magenta Studio, a suite of free music-making tools using Magenta's machine learning models. Available as an Ableton plugin or as standalone Electron apps. Launched Nov 2018.
- Runway, a toolkit that adds artificial intelligence capabilities to design and creative platforms. Built by Cristóbal Valenzuela. First alpha released May 2018.
- GAN Playground - Explore Generative Adversarial Nets in your Browser, by Reiichiro Nakano, 2017.
- Magenta demos
Datasets
- Google Dataset Search
- Luke de Oliveira, "Fueling the Gold Rush: The Greatest Public Datasets for AI", Medium, 11 Feb 2017.
- Magenta datasets
- See also
- Madhumita Murgia, "Microsoft quietly deletes largest public face recognition data set", The Financial Times, 6 Jun 2019.
Courses and textbooks for artists
- Textbooks
- Francis Tseng, "Notes on Artificial Intelligence", started Fall 2015.
- Gene Kogan, Francis Tseng, Machine Learning for Artists, 2016f. Book in progress.
- Video lectures
- Gene Kogan, "Machine Learning for Artists", course taught at ITP, New York University, New York, Spring 2016. 6 lectures, ~15 hours. Announcement.
- Gene Kogan, "The Neural Aesthetic", course taught at School Of Machines, Making, and Make-Believe, Berlin, Summer 2016. 8 lectures, ~18 hours.
- Gene Kogan, "The Neural Aesthetic", course taught at ITP, New York University, New York, Fall 2018. 12 lectures.
- Introductions
- Kyle McDonald, "A Return to Machine Learning", Medium, 7 Oct 2016.
- MOOC
- Rebecca Fiebrink, Machine Learning for Musicians and Artists, Goldsmiths University of London. Launched 2016.
- Resources
- A.I. Experiments, a resource on machine learning art developed by Alexander Chen, creative director at Google Creative Lab, with Yotam Mann, C Christiansen, Jonas Jongejan, Gene Kogan, Kyle McDonald, et al. Launched on 16 Nov 2016.
- Kailash Ahirwar, Important resources if you are working with Neural Style Transfer or Deep Photo Style Transfer, Medium, 20 Aug 2017.
- Artificial Intelligence and Media Philosophy (KIM) courses, HfG Karlsruhe, 2017ff.
- People + AI Research, Google Design, 2018ff.
Research papers
- Memo Akten, Mick Grierson, "Collaborative Creativity with Monte-Carlo Tree Search and Convolutional Neural Networks", Dec 2016.
- Memo Akten, Mick Grierson, "Real-Time Interactive Sequence Generation and Control with Recurrent Neural Network Ensembles", Dec 2016.
- Pilar Rosado, "Computer Vision Models to Categorize Art Collections According to the Visual Content: A New Approach to the Abstract Art of Antoni Tàpies", Leonardo, Feb 2017. Based on PhD from U Barcelona, 2015. [29]
- Ahmed Elgammal, Bingchen Liu, Mohamed Elhoseiny, Marian Mazzone, "CAN: Creative Adversarial Networks, Generating 'Art' by Learning About Styles and Deviating from Style Norms", Jun 2017.
- Daniel Berio, Memo Akten, Frederic Fol Leymarie, Mick Grierson, Réjean Plamondon, "Calligraphic Stylisation Learning with a Physiologically Plausible Model of Movement and Recurrent Neural Networks", Sep 2017.
- Ahmed Elgammal, Yan Kang, Milko Den Leeuw, "Picasso, Matisse, or a Fake? Automated Analysis of Drawings at the Stroke Level for Attribution and Authentication", Nov 2017.
- Ahmed Elgammal, Marian Mazzone, Bingchen Liu, Diana Kim, Mohamed Elhoseiny, "The Shape of Art History in the Eyes of the Machine", Jan 2018.
- Magenta research papers, [30]
Scientific introduction into deep learning
- Ethem Alpaydin, Introduction to Machine Learning, MIT Press, 2004, 400 pp; 2nd ed., 2009, 584 pp; 3rd ed., 2014, 640 pp.
- Christopher M. Bishop, [Pattern Recognition and Machine Learning], Springer, 2011, 738 pp.
- Michael Nielsen, Neural Networks and Deep Learning, Determination Press, 2015.
- Ian Goodfellow, Yoshua Bengio, Aaron Courville, Deep Learning, MIT Press, 2016.
- Ethem Alpaydin, Machine Learning: The New AI, MIT Press, 2016, 224 pp. [31]
Historization of deep learning
- Jürgen Schmidhuber, "Deep Learning in Neural Networks: An Overview", ScienceDirect 61, Jan 2015, pp 85-117. [32]
- Yann LeCun, Yoshua Bengio, Geoffrey Hinton, "Deep Learning", Nature 521, 28 May 2015, pp 436-444. Critiqued by Schmidhuber recasting the recent advances of deep learning as building on top of prior work with multilayer neural networks, going back decades.
- Andrey Kurenkov, "A 'Brief' History of Neural Nets and Deep Learning", Part 2, Part 3, Part 4, Andrey Kurenkov blog, 24 Dec 2015.
- Stephanie Dick, "Artificial Intelligence", Harvard Data Science Review 1, 23 Jun 2019.