Difference between revisions of "El Lissitzky"
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
[[Image:Photograph_of_El_Lissitzky_his_wife_Sophie_Lissitzky-Kueppers_and_their_child.jpg|thumb|258px|Lissitzky with his wife Sophie Lissitzky-Küppers and their child]] | [[Image:Photograph_of_El_Lissitzky_his_wife_Sophie_Lissitzky-Kueppers_and_their_child.jpg|thumb|258px|Lissitzky with his wife Sophie Lissitzky-Küppers and their child]] | ||
[[Image:Lissitzky_El_1924_Proun_99.jpg|thumb|258px|El Lissitzky, ''Proun 99'', water-soluble and metallic paint on wood, 129x99cm, 1924.]] | [[Image:Lissitzky_El_1924_Proun_99.jpg|thumb|258px|El Lissitzky, ''Proun 99'', water-soluble and metallic paint on wood, 129x99cm, 1924.]] | ||
| − | El Lissitzky was | + | El Lissitzky was an artist, designer, photographer, typographer, polemicist and architect. He was an important figure of the Russian avant-garde, helping develop suprematism with his mentor, [[Kazimir Malevich]], and designing numerous exhibition displays and propaganda works for the Soviet Union. His work greatly influenced the Bauhaus and constructivist movements, and he experimented with production techniques and stylistic devices that would go on to dominate 20th-century graphic design. |
==Life and work== | ==Life and work== | ||
===Early years=== | ===Early years=== | ||
| − | Born '''Lazar Markovich (El) Lissitzky''' (Ла́зарь Ма́ркович Лиси́цкий) in 1890 to | + | Born '''Lazar Markovich (El) Lissitzky''' (Ла́зарь Ма́ркович Лиси́цкий) in 1890 to an educated middle-class Jewish family in Pochinok, Smolensk Province, Russia. He grew up in Vitebsk, a small Jewish town in Belorussia, where he took art lessons in 1903 from Russian painter Iurii (Yehuda) Moiseevich Pen, who also taught [[Marc Chagall]]. In 1909, after being turned down by the St. Petersburg Academy of Art, Lissitzky left Russia for the first time to enroll at the Technische Hochschule in Darmstadt, Germany, where he studied architectural engineering. During his studies, in 1912 he traveled in Germany and also to France and Italy, but was forced to return to Russia during the summer of 1914, after the outbreak of World War I. He enrolled as a student of engineering and architecture at the Riga Polytechnical Institute [Rizhskii politekhnicheskii institut], temporarily quartered in Moscow, and received his diploma on 3 June 1918 with the degree of engineer-architect. In 1915-16 he worked in various architectural offices in Moscow and St. Petersburg.<ref>{{harvnb|PerloffReed|2003|p=6}}</ref><ref>{{harvnb|Nisbet|1987|p=14}}</ref> |
| − | organized by the Jewish Historical and Ethnographic Society to | + | |
| + | In 1916 Lissitzky became deeply involved in a Russian national movement to create a revival of Yiddish culture for modern Russian Jews. With the artist Issachar Ryback, he set off on an expedition organized by the Jewish Historical and Ethnographic Society [Evreiskoe istorichesko-etnograficheskoe obshchestvo] to study and record the ornamentation and inscriptions in synagogues located along the Dnieper River. Following the February Revolution of 1917, Lissitzky moved from Moscow to Kiev where he devoted himself to the illustration of Yiddish books, especially for children, and organised and submitted work for exhibitions of Jewish art in Moscow. In early 1919, he helped found the publishing house Kultur-Lige, which became a leading force in the dissemination of Yiddish culture in Ukraine. Toward the end of his stay in Kiev, Lissitzky worked for the art section of the local branch of [[IZO|IZO Narkompros]].<ref>{{harvnb|PerloffReed|2003|pp=6-7}}</ref> | ||
===Vitebsk and Moscow (1919-21)=== | ===Vitebsk and Moscow (1919-21)=== | ||
| − | + | Lissitzky's move in July 1919 from the relative isolation of the Bolshevik-controlled city of Kiev back to Vitebsk brought with it a shift in focus from Yiddish culture to architecture and book design. At the invitation of [[Marc Chagall]], Lissitzky began a new position teaching architecture, graphic arts, and printing at the [[Vitebsk Popular Art Institute]]. In September, he was joined by [[Kazimir Malevich]], whose system of nonobjective art, [[suprematism]], inspired Lissitzky to take up painting and to invent his own form of abstract art, which he named ''Proun'' [Proekt utverzhdenia novogo; Project for the Affirmation of the New] in 1920. Propaganda also became a more overt part of Lissitzky's artistic mission at this time; during the civil war, he worked in the suprematist collective [[UNOVIS]] [Affirmers of the New Art] as a designer of agitational posters meant to incite workers back to the factory benches and to rally Jews around Bolshevism.<ref>{{harvnb|PerloffReed|2003|p=7}}</ref> | |
| + | |||
| + | After disagreements between Chagall and Malevich led to the disbandment of the Institute in 1921, Lissitzky returned to Moscow to teach architecture at the newly established [[VKhUTEMAS]]. This was a period of great artistic ferment and debate in Moscow. Lissitzky's arrival coincided with the emergence of the radical First Working Group of Constructivists, which advocated a utilitarian and socialist platform of art for industry. In September 1921, at [[INKhUK]], Lissitzky put forth his own program in an important lecture, outlining the connections between suprematist painting and the principles of space and construction in his ''Proun'' works.<ref>{{harvnb|PerloffReed|2003|p=7}}</ref> | ||
===Germany and Switzerland (1921-25)=== | ===Germany and Switzerland (1921-25)=== | ||
| − | December 1921 | + | In December 1921, Lissitzky left Russia for Berlin, by way of Warsaw, dispatched by the Soviet government to establish cultural contacts between Soviet and German artists. In 1922 he collaborated with the Russian writer [[Ilya Ehrenburg]] on producing two issues of the short-lived periodical ''[[Veshch/Objet/Gegenstand]]''; met the typographer [[Jan Tschichold]] who became his life-long friend. In May 1922 Lissitzky participated in the [[Congress of International Progressive Artists]] in Düsseldorf; followed by the [[Congress of the Constructivists and Dadaists]] in Weimar in September, where he met the Dada artist [[Kurt Schwitters]]. He had a minor role in setting up the [[First Russian Art Exhibition]] in Berlin in October, when he also met [[Sophie Küppers]], who had been the artistic director of the Kestner Society in Hanover, founded by her recently deceased husband Paul Erich Küppers to support and promote the German avant-garde. In December 1922 he delivered an important lecture in Berlin on Soviet art, the next year followed by the lectures in Rotterdam, Utrecht, The Hague and at the Kestner Society. In 1923, Lissitzky also shortly joined the editorial board of [[Hans Richter]]’s journal ''G''; became a member of the [[De Stijl]] group; and joined [[ASNOVA]] (Association of the New Architects), an organization founded in Moscow by [[Nikolai Ladovsky]], [[Nikolai Dokuchaev]] and [[Vladimir Krinsky]], assuming responsibility for developing connections with foreign architects. |
| + | |||
| + | In October 1923 he was taken ill with acute pneumonia, a few weeks later diagnosed with pulmonary tuberculosis, and in February 1924 relocated to a sanatorium near Locarno, Switzerland, where, with the help of his future wife Sophie, he produced publications and photographs at a remarkable pace: edited the architectural review ''ABC: Beiträge zum Bauen'' with the Dutch architect [[Mart Stam]] and the Swiss architect [[Emil Roth]]; produced advertising designs for Gunther Wagner's Pelikan office supply company; and with the technical help of Roth, began work on the ''Wolkenbügel'' [Cloud Iron], a horizontally expanding skyscraper intended for the Nikitsky Square in Moscow. In November 1924 the Swiss authorities turned down his request to renew his visa, but grant him a six-month extension "on humanitarian grounds." | ||
===Exhibition work in Germany and Russia=== | ===Exhibition work in Germany and Russia=== | ||
| − | June 1925 | + | In June 1925 Lissitzky returned to Moscow via St Petersburg. In January 1926 he was appointed head of the Department of Furniture and Interior Design for the wood and metal workshop at [[VKhUTEMAS]]. Later in June he received assignment from [[Narkompros]] to travel to Dresden, Rotterdam, Utrecht, Hamburg, and Lübeck to study modern architecture. In Germany, he was commissioned by the directorate of the International Art Exhibition in Dresden to design the ''Raum für konstruktive Kunst'' [Room for Constructivist Art] (1926), and by Alexander Dorner to design the ''Kabinett der Abstrakten'' [Abstract Cabinet] for the Provinzialmuseum (Sprengel Museum) in Hanover (1927–28). In collaboration with Ladovsky, Lissitzky published the single issue of the architectural review ''ASNOVA'' in Moscow, 1926. |
| + | |||
| + | By 1927, with the success of his design for the All-Union Printing Trades Exhibition in Moscow, Lissitzky had became a much sought-after propagandist for the Stalinist regime, realising the Soviet Pavilion at the International Press Exhibition in Cologne (1928), the Soviet Room at the Film and Photo Exhibition in Stuttgart (1929), the Soviet Pavilion at the International Hygiene Exhibition in Dresden (1930), the Soviet section at the International Fur Trade Exhibition in Leipzig (1930), and the Gorky Park of Culture and Rest in Moscow (1931). | ||
| + | |||
| + | On 27 January 1927 Lissitzky married Sophie Küppers; his son, Jen, was born on 12 October 1930; and the next year Sophie’s older sons come to Russia to live with her and Lissitzky in the village of Khodnya, thirty miles from Moscow. During a 1928 vacation in Austria and Paris Lissitzky met [[Piet Mondrian]], [[Fernand Léger]] and [[Le Corbusier]]. | ||
===Later years=== | ===Later years=== | ||
| − | 1932 | + | In 1932 Lissitzky signed his first contract with the editors of ''USSR im Bau'' [USSR in Construction], a Soviet propaganda publication intended for Western audiences and published in Russian, English, German, and French; became one of the principal artists for the journal, along with [[Aleksandr Rodchenko]], [[Varvara Stepanova]], and [[Solomon Telingater]]; designed seventeen issues, ten of them in collaboration with Sophie Küppers. In 1934 he was appointed chief artist for the Agricultural Exhibition of the Soviet Union in Moscow. During 1935-36 Lissitzky was frequently hospitalized; convalesced in a sanatorium in the Caucasus. In 1940 he was appointed chief artist for the Soviet Pavilion at the ''Belgrade International Exhibition'', a project left unfinished due to the outbreak of World War II. In 1941 he worked on anti-Nazi posters and other war-related projects until his death in Moscow on 30 December. |
==Portraits== | ==Portraits== | ||
| Line 115: | Line 124: | ||
[http://www.fondationlecorbusier.fr/ Fondation Le Corbusier] in Paris has three letters from 1924 between [[Le Corbusier]] and Lissitzky. | [http://www.fondationlecorbusier.fr/ Fondation Le Corbusier] in Paris has three letters from 1924 between [[Le Corbusier]] and Lissitzky. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Notes== | ||
| + | {{Reflist|4}} | ||
==Literature== | ==Literature== | ||
| + | {{refbegin}} | ||
===By Lissitzky=== | ===By Lissitzky=== | ||
| − | + | [[Image:Lissitzky_El_1922_Suprematisch_worden_van_2_kwadraten_in_6_konstrukties_cover.jpg|thumb|258px|''Suprematisch worden van 2 kwadraten in 6 konstrukties'', 1922. [[Media:Lissitzky_El_1922_Suprematisch_worden_van_2_kwadraten_in_6_konstrukties.pdf|Download]].]] | |
| − | |||
| − | [[Image:Lissitzky_El_1922_Suprematisch_worden_van_2_kwadraten_in_6_konstrukties_cover.jpg|thumb|258px| | ||
[[Image:Mayakovsky_Vladimir_Lissitzky_El_Dlia_golosa_cover.jpg|thumb|258px|Vladimir Mayakovsky, El Lissitzky, ''For the Voice'', 1923. [[Media:Mayakovsky_Vladimir_Lissitzky_El_Dlia_golosa.pdf|Download]].]] | [[Image:Mayakovsky_Vladimir_Lissitzky_El_Dlia_golosa_cover.jpg|thumb|258px|Vladimir Mayakovsky, El Lissitzky, ''For the Voice'', 1923. [[Media:Mayakovsky_Vladimir_Lissitzky_El_Dlia_golosa.pdf|Download]].]] | ||
| − | [[Image:Lissitzky_El_1923_Figurinenmappe_Sieg_ueber_die_Sonne_cover.jpg|thumb|258px| | + | [[Image:Lissitzky_El_1923_Figurinenmappe_Sieg_ueber_die_Sonne_cover.jpg|thumb|258px|''Figurinenmappe: Sieg über die Sonne'', 1923. [[Media:Lissitzky_El_1923_Figurinenmappe_Sieg_ueber_die_Sonne.pdf|Download]].]] |
| − | [[Image:Lissitzky_El_1923_1o_Kestnermappe_Proun_cover.jpg|thumb|258px| | + | [[Image:Lissitzky_El_1923_1o_Kestnermappe_Proun_cover.jpg|thumb|258px|''1o Kestnermappe Proun'', 1923. [[Media:Lissitzky_El_1923_1o_Kestnermappe_Proun.pdf|Download]].]] |
[[Image:Merz_Vol_2_No_8-9_April-June_1924_cover.jpg|thumb|258px|El Lissitzky, Kurt Schwitters (eds.), ''Merz'' 2:8/9 (April-June 1924): "Nasci". [[Media:Merz_Vol_2_No_8-9_April-June_1924.pdf|Download]].]] | [[Image:Merz_Vol_2_No_8-9_April-June_1924_cover.jpg|thumb|258px|El Lissitzky, Kurt Schwitters (eds.), ''Merz'' 2:8/9 (April-June 1924): "Nasci". [[Media:Merz_Vol_2_No_8-9_April-June_1924.pdf|Download]].]] | ||
[[Image:Lissitzky_El_Arp_Hans_Die_Kunstismen_1914-1924_cover.jpg|thumb|258px|El Lissitzky, Hans Arp, ''Die Kunstismen/Les Ismes De L’Art/The Isms of Art: 1914-1924'', 1925. [[Media:Lissitzky_El_Arp_Hans_Die_Kunstismen_1914-1924_pp_I-VII.pdf|Download pages I-VII]].]] | [[Image:Lissitzky_El_Arp_Hans_Die_Kunstismen_1914-1924_cover.jpg|thumb|258px|El Lissitzky, Hans Arp, ''Die Kunstismen/Les Ismes De L’Art/The Isms of Art: 1914-1924'', 1925. [[Media:Lissitzky_El_Arp_Hans_Die_Kunstismen_1914-1924_pp_I-VII.pdf|Download pages I-VII]].]] | ||
| − | + | * ''[[Media:Lissitzky_El_1922_Suprematisch_worden_van_2_kwadraten_in_6_konstrukties.pdf|Suprematisch worden van 2 kwadraten in 6 konstrukties]]'', ed. Theo van Doesburg, Hague, 1922. Produced in 50 copies, appeared in ''De Stijl'' 5 (1922) 10/11. (in Dutch). [http://brbl-dl.library.yale.edu/vufind/Record/3447393] | |
| − | |||
| − | * ''[[Media:Lissitzky_El_1922_Suprematisch_worden_van_2_kwadraten_in_6_konstrukties.pdf|Suprematisch worden van 2 kwadraten in 6 konstrukties]]'', ed. Theo van Doesburg, Hague, 1922. Produced in 50 copies, appeared in ''De Stijl'' 5 | ||
* with Vladimir Mayakovsky, ''[[Media:Mayakovsky_Vladimir_Lissitzky_El_Dlia_golosa.pdf|Для голоса]]'' [Dlia golosa; For the Voice], Berlin: R.S.F.S.R. Gosudarstvennoe Izdatel’stvo, 1923, 61 pp. A collection of 13 poems by Mayakovsky, "constructed" by Lissitzky, printed in 3000 copies by Lutze & Vogt, Berlin. [http://brbl-dl.library.yale.edu/vufind/Record/3565558] | * with Vladimir Mayakovsky, ''[[Media:Mayakovsky_Vladimir_Lissitzky_El_Dlia_golosa.pdf|Для голоса]]'' [Dlia golosa; For the Voice], Berlin: R.S.F.S.R. Gosudarstvennoe Izdatel’stvo, 1923, 61 pp. A collection of 13 poems by Mayakovsky, "constructed" by Lissitzky, printed in 3000 copies by Lutze & Vogt, Berlin. [http://brbl-dl.library.yale.edu/vufind/Record/3565558] | ||
* ''[[Media:Lissitzky_El_1923_Figurinenmappe_Sieg_ueber_die_Sonne.pdf|Figurinenmappe: Sieg über die Sonne]]'' [Figurines: Victory Over the Sun], Hanover: Leunis & Chapman, 1923. The drawings recasting the Russian Futurist opera ''[[Victory Over the Sun]]'' (1913/20) as an electromechanical show with mechanical puppets. [http://www.museum-digital.de/san/index.php?t=serie&serges=59] [http://www.dataisnature.com/?p=1907] [http://www.getty.edu/research/tools/guides_bibliographies/lissitzky/6_victory/index.html] | * ''[[Media:Lissitzky_El_1923_Figurinenmappe_Sieg_ueber_die_Sonne.pdf|Figurinenmappe: Sieg über die Sonne]]'' [Figurines: Victory Over the Sun], Hanover: Leunis & Chapman, 1923. The drawings recasting the Russian Futurist opera ''[[Victory Over the Sun]]'' (1913/20) as an electromechanical show with mechanical puppets. [http://www.museum-digital.de/san/index.php?t=serie&serges=59] [http://www.dataisnature.com/?p=1907] [http://www.getty.edu/research/tools/guides_bibliographies/lissitzky/6_victory/index.html] | ||
| Line 142: | Line 151: | ||
* [http://rosswolfe.wordpress.com/2013/09/16/proun/ "Тезисы к ПРОУНу (от живописи к архитектуре)"], 1920. (in Russian) | * [http://rosswolfe.wordpress.com/2013/09/16/proun/ "Тезисы к ПРОУНу (от живописи к архитектуре)"], 1920. (in Russian) | ||
** [http://rosswolfe.wordpress.com/2013/09/16/proun/ "Theses on the PROUN: From Painting to Architecture"]. | ** [http://rosswolfe.wordpress.com/2013/09/16/proun/ "Theses on the PROUN: From Painting to Architecture"]. | ||
| − | * with Ilya Ehrenberg, [ | + | * with Ilya Ehrenberg, [[Media:Lissitzky_El_Ehrenberg_Ilya_1922_Statement_by_the_Editors_of_Veshch.pdf|"Statement by the Editors of Veshch"]], 1922. |
| − | |||
| − | |||
* [[Media:G_Material_zur_elementaren_Gestaltung_1_Jul_1923.pdf|"Prounenraum, Grosse Berliner Kunstausstellung"]], ''G: Material zur elementaren Gestaltung'' 1 (July 1923). (in German) | * [[Media:G_Material_zur_elementaren_Gestaltung_1_Jul_1923.pdf|"Prounenraum, Grosse Berliner Kunstausstellung"]], ''G: Material zur elementaren Gestaltung'' 1 (July 1923). (in German) | ||
* [http://books.google.com/books?id=duTDMRa8bs4C&pg=PA106 "Wheel - Propeller and What Will Follow: Our Form-Production Is a Function of Our System of Movement"], ''G: Material zur elementaren Gestaltung'' 2 (September 1923), p 2. | * [http://books.google.com/books?id=duTDMRa8bs4C&pg=PA106 "Wheel - Propeller and What Will Follow: Our Form-Production Is a Function of Our System of Movement"], ''G: Material zur elementaren Gestaltung'' 2 (September 1923), p 2. | ||
* [http://modernistarchitecture.wordpress.com/2010/10/21/el-lissitzky%E2%80%99s-%E2%80%9Carchitecture-in-the-ussr%E2%80%9D-1925/ "Architecture in the USSR"], ''Die Kunstblatt'' 2 (February 1925). Trans. David Britt, in ''El Lissitzky: Life, Letters, Texts''. | * [http://modernistarchitecture.wordpress.com/2010/10/21/el-lissitzky%E2%80%99s-%E2%80%9Carchitecture-in-the-ussr%E2%80%9D-1925/ "Architecture in the USSR"], ''Die Kunstblatt'' 2 (February 1925). Trans. David Britt, in ''El Lissitzky: Life, Letters, Texts''. | ||
| − | * [http://modernistarchitecture.wordpress.com/2011/06/23/el-lissitzkys-%E2%80%98americanism%E2%80%99-in-european-architecture-1925/ "‘Americanism’ in European Architecture"], ''Krasnaya Niva'' 49, 1925. Trans. Sophie Lissitzky- | + | * [http://modernistarchitecture.wordpress.com/2011/06/23/el-lissitzkys-%E2%80%98americanism%E2%80%99-in-european-architecture-1925/ "‘Americanism’ in European Architecture"], ''Krasnaya Niva'' 49, 1925. Trans. Sophie Lissitzky-Küppers, in ''El Lissitzky: Life, Letters, Texts''. |
* [[Media:Lissitzky_El_1925_A_and_Pangeometry.pdf|"A. and Pangeometry"]], 1925. | * [[Media:Lissitzky_El_1925_A_and_Pangeometry.pdf|"A. and Pangeometry"]], 1925. | ||
* [[Media:Lissitzky_El_1926_The_Future_of_the_Book.pdf|"The Future of the Book"]], 1926. Trans. from ''New Left Review'' 41, 1967, pp 39-44. | * [[Media:Lissitzky_El_1926_The_Future_of_the_Book.pdf|"The Future of the Book"]], 1926. Trans. from ''New Left Review'' 41, 1967, pp 39-44. | ||
| Line 154: | Line 161: | ||
* "Vicking Eggeling", ''Izvestiya Asnova'' 1, 1926. | * "Vicking Eggeling", ''Izvestiya Asnova'' 1, 1926. | ||
* [[Media:Lissitzky_El_1926_der_Lebensfilm_von_el_bis_1926.pdf|"der Lebensfilm von el, bis 1926"]], 1926, 2 pp. (in German). An autobiographical note. [http://brbl-dl.library.yale.edu/vufind/Record/3542791] | * [[Media:Lissitzky_El_1926_der_Lebensfilm_von_el_bis_1926.pdf|"der Lebensfilm von el, bis 1926"]], 1926, 2 pp. (in German). An autobiographical note. [http://brbl-dl.library.yale.edu/vufind/Record/3542791] | ||
| − | |||
===On Lissitzky=== | ===On Lissitzky=== | ||
| Line 162: | Line 168: | ||
* Margarita Tupitsyn, ''El Lissitzky: Beyond the Abstract Cabinet: Photography, Design, Collaboration'', New Haven/London: Yale University Press, 1999, 239 pp. | * Margarita Tupitsyn, ''El Lissitzky: Beyond the Abstract Cabinet: Photography, Design, Collaboration'', New Haven/London: Yale University Press, 1999, 239 pp. | ||
** ''El Lissitzky: Jenseits der Abstraktion, Fotografie, Design, Kooperation'', Munich: Schimer/Mosel, 1999, 239 pp. (in German) | ** ''El Lissitzky: Jenseits der Abstraktion, Fotografie, Design, Kooperation'', Munich: Schimer/Mosel, 1999, 239 pp. (in German) | ||
| − | * Nancy Lynn | + | * {{cite book|ref=harv|editor-last=Perloff|editor-first=Nancy Lynn|editor2-last=Reed|editor2-first=Brian|title=Situating El Lissitzky: Vitebsk, Berlin, Moscow|year=2003|publisher=Getty Publications}} [http://getty.edu/research/publications/pdfs/2003situate_lissitsky.pdf Contents], [http://books.google.com/books?id=CRtv3Pxz3V0C] |
** Nancy Perloff, [[Media:Perloff_Nancy_2003_The_Puzzle_of_El_Lissitzkys_Artistic_Identity.pdf|"The Puzzle of El Lissitzky's Artistic Identity"]], pp 1-23. | ** Nancy Perloff, [[Media:Perloff_Nancy_2003_The_Puzzle_of_El_Lissitzkys_Artistic_Identity.pdf|"The Puzzle of El Lissitzky's Artistic Identity"]], pp 1-23. | ||
** Christina Lodder, [[Media:Lodder_Christina_2003_El_Lissitzky_and_the_Export_of_Constructivism.pdf|"El Lissitzky and the Export of Constructivism"]], pp 27-46. | ** Christina Lodder, [[Media:Lodder_Christina_2003_El_Lissitzky_and_the_Export_of_Constructivism.pdf|"El Lissitzky and the Export of Constructivism"]], pp 27-46. | ||
| Line 177: | Line 183: | ||
* Franz Roh, Jan Tschichold (eds.), ''Foto-Auge / Oeil et Photo / Photo-Eye'', Stuttgart: Akademischer Verlag Dr. Fritz Wedekind, 1929, 77 pp, 78 photographs. (in German, French and English). A photobook based on the ''Film und Foto'' exhibition organised by the Deutscher Werkbund in Stuttgart in 1929. The front-cover shows El Lissitzky's self-portrait (Küppers, plate 114). Includes works by Baumeister, Max Ernst, G. Grosz, Heartfield, Teige, Moholy-Nagy, Edward Weston, Peter Hans, Renger-Patzsch, Hans Leistikow, Willi Baumeister, Walter Funkat, Dsiga Wertoff. The book features various techniques of photography eg. photogram, x-rays-photo, photomontage. Designed by Jan Tschichold. [http://lib.stanford.edu/art-architecture-library/roh-franz-and-jan-tschichold-foto-auge-oeil-et-photo-photo-eye] [http://wiedler.ch/felix/books/story/680] | * Franz Roh, Jan Tschichold (eds.), ''Foto-Auge / Oeil et Photo / Photo-Eye'', Stuttgart: Akademischer Verlag Dr. Fritz Wedekind, 1929, 77 pp, 78 photographs. (in German, French and English). A photobook based on the ''Film und Foto'' exhibition organised by the Deutscher Werkbund in Stuttgart in 1929. The front-cover shows El Lissitzky's self-portrait (Küppers, plate 114). Includes works by Baumeister, Max Ernst, G. Grosz, Heartfield, Teige, Moholy-Nagy, Edward Weston, Peter Hans, Renger-Patzsch, Hans Leistikow, Willi Baumeister, Walter Funkat, Dsiga Wertoff. The book features various techniques of photography eg. photogram, x-rays-photo, photomontage. Designed by Jan Tschichold. [http://lib.stanford.edu/art-architecture-library/roh-franz-and-jan-tschichold-foto-auge-oeil-et-photo-photo-eye] [http://wiedler.ch/felix/books/story/680] | ||
* ''El Lissitzky'', Cologne: Galerie Gmurzynska, 1976. | * ''El Lissitzky'', Cologne: Galerie Gmurzynska, 1976. | ||
| − | * | + | * {{cite book|ref=harv|editor-last=Nisbet|editor-first=Peter|title=El Lissitzky, 1890-1941|year=1987|publisher=Harvard University Art Museums, Busch-Reisinger Museum|location=Cambridge, MA}} |
* ''[http://adkp.ruhe.ru/sites/default/files/0306.pdf El Lissitzky and Alexander Dorner: Kabinett der Abstrakten – Original and Facsimile]'', Berlin: Museum of American Art, 2009, 32 pp. | * ''[http://adkp.ruhe.ru/sites/default/files/0306.pdf El Lissitzky and Alexander Dorner: Kabinett der Abstrakten – Original and Facsimile]'', Berlin: Museum of American Art, 2009, 32 pp. | ||
| Line 196: | Line 202: | ||
* Victor Margolin, ''The Struggle for Utopia: Rodchenko, Lissitzky, Moholy-Nagy, 1917-1946'', University of Chicago Press, 1998. [http://books.google.com/books?id=q93LHoimzjcC] | * Victor Margolin, ''The Struggle for Utopia: Rodchenko, Lissitzky, Moholy-Nagy, 1917-1946'', University of Chicago Press, 1998. [http://books.google.com/books?id=q93LHoimzjcC] | ||
* Paul Galvez, [[Media:Galvez_Paul_2000_Self-Portrait_of_the_Artist_as_a_Monkey-Hand.pdf|"Self-Portrait of the Artist as a Monkey-Hand"]], ''October'' 93, 2000. | * Paul Galvez, [[Media:Galvez_Paul_2000_Self-Portrait_of_the_Artist_as_a_Monkey-Hand.pdf|"Self-Portrait of the Artist as a Monkey-Hand"]], ''October'' 93, 2000. | ||
| − | |||
* Igor Dukhan, [[Media:Dukhan_Igor_2007_El_Lissitzky_Jewish_as_Universal_From_Jewish_Style_to_Pangeometry.pdf|"El Lissitzky: Jewish as Universal: From Jewish Style to Pangeometry"]], ''Ars Judaica'', 2007, pp 1-20. | * Igor Dukhan, [[Media:Dukhan_Igor_2007_El_Lissitzky_Jewish_as_Universal_From_Jewish_Style_to_Pangeometry.pdf|"El Lissitzky: Jewish as Universal: From Jewish Style to Pangeometry"]], ''Ars Judaica'', 2007, pp 1-20. | ||
* Alexandra Shatskikh, ''Vitebsk: The Life of Art'', Yale University Press, 2007. | * Alexandra Shatskikh, ''Vitebsk: The Life of Art'', Yale University Press, 2007. | ||
| + | * Seth L. Wolitz, [http://www.yivoencyclopedia.org/article.aspx/Lissitzky_El "El Lissitzky"], ''The Yivo Encyclopedia of Jews in Eastern Europe'', c2010. | ||
* John G. Hatch, [[Media:Hatch_John_G_2010_Some_Adaptations_of_Relativity_in_the_1920s_and_the_Birth_of_Abstract_Architecture.pdf|"Some Adaptations of Relativity in the 1920s and the Birth of Abstract Architecture"]], ''Nexus Network Journal'' 12:1, 2010, pp 131–147. | * John G. Hatch, [[Media:Hatch_John_G_2010_Some_Adaptations_of_Relativity_in_the_1920s_and_the_Birth_of_Abstract_Architecture.pdf|"Some Adaptations of Relativity in the 1920s and the Birth of Abstract Architecture"]], ''Nexus Network Journal'' 12:1, 2010, pp 131–147. | ||
* Maria Gough, "Contains Graphic Material: El Lissitzky and the Topography of ''G''", in ''G: An Avant-Garde Journal of Art, Architecture, Design, and Film, 1923-1926'', eds. Detlef Mertins and Michael William Jennings, Getty Publications, 2010, pp 21-52. | * Maria Gough, "Contains Graphic Material: El Lissitzky and the Topography of ''G''", in ''G: An Avant-Garde Journal of Art, Architecture, Design, and Film, 1923-1926'', eds. Detlef Mertins and Michael William Jennings, Getty Publications, 2010, pp 21-52. | ||
| + | * Maria Gough, "The Abstract Environment", in ''Inventing Abstraction, 1910-1925: How a Radical Idea Changed Modern Art'', eds. Leah Dickerman and Matthew Affron, New York: Museum of Modern Art, 2012, pp 310-323. [http://books.google.com/books?id=2NNb9bUe4bIC&pg=PA310] | ||
; Theses | ; Theses | ||
| + | * Alan C. Birnholz, ''El Lissitzky'', Yale University, 1973. Ph.D. dissertation. | ||
| + | * Peter Nisbet, ''El Lissitzky in the Proun Years: A Study of His Work and Thought, 1917–1927'', Yale University, 1995, 599 pp. Ph.D. dissertation. [http://access.cjh.org/home.php?type=extid&term=1633800#1] | ||
* Kemal Reha Kavas, ''[http://etd.lib.metu.edu.tr/upload/12605911/index.pdf Architectural Form Generation in Suprematist Painterly Space: The Significance of El Lissitzky's Prouns]'', Middle East Technical University, 2005, 120 pp. Master Thesis. | * Kemal Reha Kavas, ''[http://etd.lib.metu.edu.tr/upload/12605911/index.pdf Architectural Form Generation in Suprematist Painterly Space: The Significance of El Lissitzky's Prouns]'', Middle East Technical University, 2005, 120 pp. Master Thesis. | ||
* Fabian Ziegler, ''[[Media:Ziegler_Fabian_2010_El_Lissitzky_Proun_Zur_Logik_der_Form.pdf|El Lissitzky - Proun. Zur Logik der Form]]'', Vienna: Vienna University, 2010, 132 pp. Master thesis. (in German) | * Fabian Ziegler, ''[[Media:Ziegler_Fabian_2010_El_Lissitzky_Proun_Zur_Logik_der_Form.pdf|El Lissitzky - Proun. Zur Logik der Form]]'', Vienna: Vienna University, 2010, 132 pp. Master thesis. (in German) | ||
| Line 208: | Line 217: | ||
; Film | ; Film | ||
* ''El Lissitzky: Constructivist of the Russian Avant-Garde'', dir. Leo Lorez, 88 min, 1989, video documentary. [http://www.original.rolandcollection.com/rolandcollection/section/16/503.htm] [http://www.rolandcollection.com/films/?prm=a12-b94-c508-d0-e0] | * ''El Lissitzky: Constructivist of the Russian Avant-Garde'', dir. Leo Lorez, 88 min, 1989, video documentary. [http://www.original.rolandcollection.com/rolandcollection/section/16/503.htm] [http://www.rolandcollection.com/films/?prm=a12-b94-c508-d0-e0] | ||
| + | {{refend}} | ||
==See also== | ==See also== | ||
| − | * [[ | + | * [[Sophie Lissitzky-Küppers]] |
| + | * [[Suprematism]] | ||
* [[Russia#Avant-garde]] | * [[Russia#Avant-garde]] | ||
| − | * [[ | + | * [[Central_and_Eastern_Europe#Constructivists.2C_Futurists|Central and Eastern Europe#Constructivists, Futurists]] |
==External links== | ==External links== | ||
| Line 233: | Line 244: | ||
{{DEFAULTSORT:Lissitzky, El}} | {{DEFAULTSORT:Lissitzky, El}} | ||
[[Category:Constructivism]] | [[Category:Constructivism]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Graphic design]] | ||
Revision as of 19:04, 30 December 2013

El Lissitzky was an artist, designer, photographer, typographer, polemicist and architect. He was an important figure of the Russian avant-garde, helping develop suprematism with his mentor, Kazimir Malevich, and designing numerous exhibition displays and propaganda works for the Soviet Union. His work greatly influenced the Bauhaus and constructivist movements, and he experimented with production techniques and stylistic devices that would go on to dominate 20th-century graphic design.
Contents
Life and work
Early years
Born Lazar Markovich (El) Lissitzky (Ла́зарь Ма́ркович Лиси́цкий) in 1890 to an educated middle-class Jewish family in Pochinok, Smolensk Province, Russia. He grew up in Vitebsk, a small Jewish town in Belorussia, where he took art lessons in 1903 from Russian painter Iurii (Yehuda) Moiseevich Pen, who also taught Marc Chagall. In 1909, after being turned down by the St. Petersburg Academy of Art, Lissitzky left Russia for the first time to enroll at the Technische Hochschule in Darmstadt, Germany, where he studied architectural engineering. During his studies, in 1912 he traveled in Germany and also to France and Italy, but was forced to return to Russia during the summer of 1914, after the outbreak of World War I. He enrolled as a student of engineering and architecture at the Riga Polytechnical Institute [Rizhskii politekhnicheskii institut], temporarily quartered in Moscow, and received his diploma on 3 June 1918 with the degree of engineer-architect. In 1915-16 he worked in various architectural offices in Moscow and St. Petersburg.[1][2]
In 1916 Lissitzky became deeply involved in a Russian national movement to create a revival of Yiddish culture for modern Russian Jews. With the artist Issachar Ryback, he set off on an expedition organized by the Jewish Historical and Ethnographic Society [Evreiskoe istorichesko-etnograficheskoe obshchestvo] to study and record the ornamentation and inscriptions in synagogues located along the Dnieper River. Following the February Revolution of 1917, Lissitzky moved from Moscow to Kiev where he devoted himself to the illustration of Yiddish books, especially for children, and organised and submitted work for exhibitions of Jewish art in Moscow. In early 1919, he helped found the publishing house Kultur-Lige, which became a leading force in the dissemination of Yiddish culture in Ukraine. Toward the end of his stay in Kiev, Lissitzky worked for the art section of the local branch of IZO Narkompros.[3]
Vitebsk and Moscow (1919-21)
Lissitzky's move in July 1919 from the relative isolation of the Bolshevik-controlled city of Kiev back to Vitebsk brought with it a shift in focus from Yiddish culture to architecture and book design. At the invitation of Marc Chagall, Lissitzky began a new position teaching architecture, graphic arts, and printing at the Vitebsk Popular Art Institute. In September, he was joined by Kazimir Malevich, whose system of nonobjective art, suprematism, inspired Lissitzky to take up painting and to invent his own form of abstract art, which he named Proun [Proekt utverzhdenia novogo; Project for the Affirmation of the New] in 1920. Propaganda also became a more overt part of Lissitzky's artistic mission at this time; during the civil war, he worked in the suprematist collective UNOVIS [Affirmers of the New Art] as a designer of agitational posters meant to incite workers back to the factory benches and to rally Jews around Bolshevism.[4]
After disagreements between Chagall and Malevich led to the disbandment of the Institute in 1921, Lissitzky returned to Moscow to teach architecture at the newly established VKhUTEMAS. This was a period of great artistic ferment and debate in Moscow. Lissitzky's arrival coincided with the emergence of the radical First Working Group of Constructivists, which advocated a utilitarian and socialist platform of art for industry. In September 1921, at INKhUK, Lissitzky put forth his own program in an important lecture, outlining the connections between suprematist painting and the principles of space and construction in his Proun works.[5]
Germany and Switzerland (1921-25)
In December 1921, Lissitzky left Russia for Berlin, by way of Warsaw, dispatched by the Soviet government to establish cultural contacts between Soviet and German artists. In 1922 he collaborated with the Russian writer Ilya Ehrenburg on producing two issues of the short-lived periodical Veshch/Objet/Gegenstand; met the typographer Jan Tschichold who became his life-long friend. In May 1922 Lissitzky participated in the Congress of International Progressive Artists in Düsseldorf; followed by the Congress of the Constructivists and Dadaists in Weimar in September, where he met the Dada artist Kurt Schwitters. He had a minor role in setting up the First Russian Art Exhibition in Berlin in October, when he also met Sophie Küppers, who had been the artistic director of the Kestner Society in Hanover, founded by her recently deceased husband Paul Erich Küppers to support and promote the German avant-garde. In December 1922 he delivered an important lecture in Berlin on Soviet art, the next year followed by the lectures in Rotterdam, Utrecht, The Hague and at the Kestner Society. In 1923, Lissitzky also shortly joined the editorial board of Hans Richter’s journal G; became a member of the De Stijl group; and joined ASNOVA (Association of the New Architects), an organization founded in Moscow by Nikolai Ladovsky, Nikolai Dokuchaev and Vladimir Krinsky, assuming responsibility for developing connections with foreign architects.
In October 1923 he was taken ill with acute pneumonia, a few weeks later diagnosed with pulmonary tuberculosis, and in February 1924 relocated to a sanatorium near Locarno, Switzerland, where, with the help of his future wife Sophie, he produced publications and photographs at a remarkable pace: edited the architectural review ABC: Beiträge zum Bauen with the Dutch architect Mart Stam and the Swiss architect Emil Roth; produced advertising designs for Gunther Wagner's Pelikan office supply company; and with the technical help of Roth, began work on the Wolkenbügel [Cloud Iron], a horizontally expanding skyscraper intended for the Nikitsky Square in Moscow. In November 1924 the Swiss authorities turned down his request to renew his visa, but grant him a six-month extension "on humanitarian grounds."
Exhibition work in Germany and Russia
In June 1925 Lissitzky returned to Moscow via St Petersburg. In January 1926 he was appointed head of the Department of Furniture and Interior Design for the wood and metal workshop at VKhUTEMAS. Later in June he received assignment from Narkompros to travel to Dresden, Rotterdam, Utrecht, Hamburg, and Lübeck to study modern architecture. In Germany, he was commissioned by the directorate of the International Art Exhibition in Dresden to design the Raum für konstruktive Kunst [Room for Constructivist Art] (1926), and by Alexander Dorner to design the Kabinett der Abstrakten [Abstract Cabinet] for the Provinzialmuseum (Sprengel Museum) in Hanover (1927–28). In collaboration with Ladovsky, Lissitzky published the single issue of the architectural review ASNOVA in Moscow, 1926.
By 1927, with the success of his design for the All-Union Printing Trades Exhibition in Moscow, Lissitzky had became a much sought-after propagandist for the Stalinist regime, realising the Soviet Pavilion at the International Press Exhibition in Cologne (1928), the Soviet Room at the Film and Photo Exhibition in Stuttgart (1929), the Soviet Pavilion at the International Hygiene Exhibition in Dresden (1930), the Soviet section at the International Fur Trade Exhibition in Leipzig (1930), and the Gorky Park of Culture and Rest in Moscow (1931).
On 27 January 1927 Lissitzky married Sophie Küppers; his son, Jen, was born on 12 October 1930; and the next year Sophie’s older sons come to Russia to live with her and Lissitzky in the village of Khodnya, thirty miles from Moscow. During a 1928 vacation in Austria and Paris Lissitzky met Piet Mondrian, Fernand Léger and Le Corbusier.
Later years
In 1932 Lissitzky signed his first contract with the editors of USSR im Bau [USSR in Construction], a Soviet propaganda publication intended for Western audiences and published in Russian, English, German, and French; became one of the principal artists for the journal, along with Aleksandr Rodchenko, Varvara Stepanova, and Solomon Telingater; designed seventeen issues, ten of them in collaboration with Sophie Küppers. In 1934 he was appointed chief artist for the Agricultural Exhibition of the Soviet Union in Moscow. During 1935-36 Lissitzky was frequently hospitalized; convalesced in a sanatorium in the Caucasus. In 1940 he was appointed chief artist for the Soviet Pavilion at the Belgrade International Exhibition, a project left unfinished due to the outbreak of World War II. In 1941 he worked on anti-Nazi posters and other war-related projects until his death in Moscow on 30 December.
Portraits
Works
- Early works
With Kazimir Malevich, Study for Backcloth for Vitebsk Committee for the Struggle against Unemployment, 1919.
- Proun
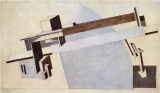
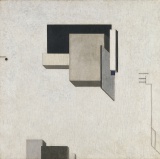
- Lissitzky El Proun 5.jpg
Proun 5
- Design of the Raum für konstruktive Kunst [Room for Constructivist Art], Internationale Kunstausstellung, Dresden, 1926
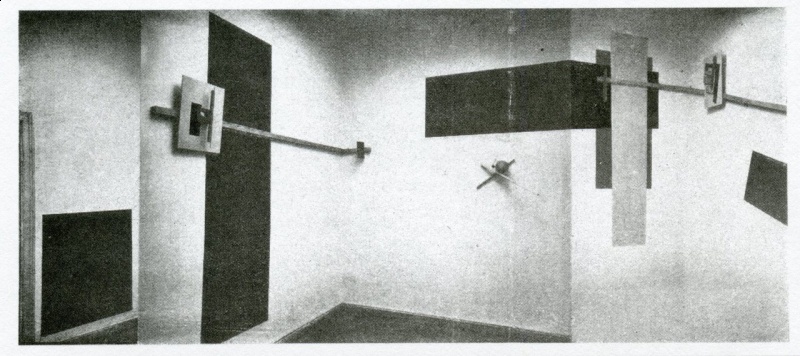
- Kabinett der Abstrakten [The Abstract Cabinet], Provinzialmuseum Hanover, 1928
Lissitzky built this modular and changeable room for abstract art in 1927–28 at the invitation of Alexander Dorner for the Landesmuseum in Hanover. The Abstract Cabinet was destroyed in 1936 during the Third Reich. [4]
- Pavilion of the Soviet Union at the Pressa exhibition, Cologne, 1928
- Other works
Collections and Archives
Russian State Archive of Literature and Art (RGALI) in Moscow possesses the most extensive collection of Lissitzky's work. Its documentary holdings on Lissitzky include a photomontage; a plan of the first skyscraper in Moscow (1924-1928); a poster of Lenin; twelve experimental photos (1920s); photos of exhibitions in Berlin and Leipzig designed by Lissitzky; various articles; a notebook of Lissitzky's with sketches and miscellaneous notes; assorted letters to Lissitzky; his birth certificate, school diploma, contracts and applications; materials on his work with the Association of New Architects; individual photos of Lissitzky (between 1922-1935); group photos with others (between 1928-1934); and two photos of Gorky taken by Lissitzky in 1928. There is a searchable CD-ROM version (1996) of the seven-volume print guide to this collection.
The Lissitzky collection at Moscow's Tretyakov Gallery consists of drawings, watercolours, lithographs, archival documents, photographs, and examples of Lissitzky's original book designs and illustrations. Of the more than 300 items, outstanding examples include his variant designs for exhibition catalogues and periodicals; covers for film scenarios; sketches, drafts, and variants of his Prouns; watercolours and drawings of costume designs; and many sketches, studies, and preparatory materials for unrealized architectural projects and exhibition pavilions.
The Lissitzky collection at Van Abbe Museum in Eindhoven consists of 130 artworks (most of which came from the artist's studio in Hanover) and is the largest outside of Russia. The Museum also possesses several archival documents relating to El Lissitzky (postcards and letters, all to architect J.J.P. Oud, dating between April 28, 1923 and December 26, 1928).
The Busch-Reisinger Museum at Harvard University, Boston, has a moderately-sized collection (41 items) consisting of drawings (12), prints (21) and books (8), with a good number of Proun images.
The Sprengel Museum in Hanover has a small collection comprised of sketches and drafts for the Abstract Cabinet, several Proun lithographs, and a few entries by Lissitzky in the 84-page guestbook of Käte Steinitz, 1920.
Rijksbureau voor Kunsthistorische Documentatie in The Hague has letters from Lissitzky to the Dutch architect and artist Theo Van Doesburg, and from Lissitzky and Kurt Schwitters to Til Brugman (all dating between 1922 and 1926).
Fondation Le Corbusier in Paris has three letters from 1924 between Le Corbusier and Lissitzky.
Notes
- ↑ PerloffReed 2003, p. 6
- ↑ Nisbet 1987, p. 14
- ↑ PerloffReed 2003, pp. 6-7
- ↑ PerloffReed 2003, p. 7
- ↑ PerloffReed 2003, p. 7
Literature
By Lissitzky






- Suprematisch worden van 2 kwadraten in 6 konstrukties, ed. Theo van Doesburg, Hague, 1922. Produced in 50 copies, appeared in De Stijl 5 (1922) 10/11. (in Dutch). [5]
- with Vladimir Mayakovsky, Для голоса [Dlia golosa; For the Voice], Berlin: R.S.F.S.R. Gosudarstvennoe Izdatel’stvo, 1923, 61 pp. A collection of 13 poems by Mayakovsky, "constructed" by Lissitzky, printed in 3000 copies by Lutze & Vogt, Berlin. [6]
- Figurinenmappe: Sieg über die Sonne [Figurines: Victory Over the Sun], Hanover: Leunis & Chapman, 1923. The drawings recasting the Russian Futurist opera Victory Over the Sun (1913/20) as an electromechanical show with mechanical puppets. [7] [8] [9]
- 1o Kestnermappe Proun [Proun. 1st Kestner Portfolio], 1923, 6 plates. A suite of lithographic prints made as a New Year gift for members of the Kestner Gesellschaft, an independent society based in Hanover, which arranged exhibitions of contemporary art. Lissitzky had had a successful exhibition at the society early in 1923 and was commissioned to produce these prints. [10]
- Editor, with Kurt Schwitters, Merz 2:8/9 (April-June 1924): "Nasci", Hanover, 18 pp. (in German/French) [11] [12]
- with Hans Arp, Die Kunstismen/Les Ismes De L’Art/The Isms of Art: 1914-1924, Erlenbach-Zürich/Munich/Leipzig: Eugen Rentsch, 1925, 46 pp. "Habe eine Idee für das letzte Merz-Heft 1924: 'Letzte Truppenschau aller Ismen von 1914-24'." schrieb El Lissitzky 1924 in einem Brief. Es gelang ihm, Hans Arp für diese Idee zu begeistern. The book gives definitions by well-known artists of the various movements, or forms of art, of the period. They range from Cubism, Futurism, Expressionism, Abstract Art, Metaphysicians, Suprematism, Simultanism, Dadaism, Purism, Neoplasticism, Merz, Proun, Perism, Constructivism, to Abstract Film. The definitions are followed by illustrations of examples of each movement. [13] [14] [15]
- Editor, Union der Sozialistischen Sowjet-Republiken: Katalog des Sowjet-Pavillons auf der Internationalen Presse-Ausstellung Koln 1928, Cologne, 1928, 111 pp, with a foldout. (in German) [16]
- Russland. Die Rekonstruktion der Architektur in der Sowjetunion, Vienna: A. Schroll, 1930, 103 pp. (in German)
- Russia: An Architecture for World Revolution, trans. Eric Dluhosch, MIT Press, 1970, 239 pp. Excerpt.
- Articles
- "Suprematism in World Reconstruction", 1920, in John E. Bowlt (ed.), Russian Art of the Avant-Garde: Theory and Criticism, 1902-1934, Viking Press, 1976, pp 151-158.
- "Тезисы к ПРОУНу (от живописи к архитектуре)", 1920. (in Russian)
- with Ilya Ehrenberg, "Statement by the Editors of Veshch", 1922.
- "Prounenraum, Grosse Berliner Kunstausstellung", G: Material zur elementaren Gestaltung 1 (July 1923). (in German)
- "Wheel - Propeller and What Will Follow: Our Form-Production Is a Function of Our System of Movement", G: Material zur elementaren Gestaltung 2 (September 1923), p 2.
- "Architecture in the USSR", Die Kunstblatt 2 (February 1925). Trans. David Britt, in El Lissitzky: Life, Letters, Texts.
- "‘Americanism’ in European Architecture", Krasnaya Niva 49, 1925. Trans. Sophie Lissitzky-Küppers, in El Lissitzky: Life, Letters, Texts.
- "A. and Pangeometry", 1925.
- "The Future of the Book", 1926. Trans. from New Left Review 41, 1967, pp 39-44.
- "Our Book", 1926. Trans. from Graphic Design Theory: Readings From the Field, ed. Helen Armstrong, Princeton, 2009, pp 25-31. Taken from El Lissitzky: Life, Letters, Text, ed. Sophie Lissitzky-Küppers, trans. Helene Aldwinckle and Mary Whittall, 1968.
- "Vicking Eggeling", Izvestiya Asnova 1, 1926.
- "der Lebensfilm von el, bis 1926", 1926, 2 pp. (in German). An autobiographical note. [17]
On Lissitzky
- Books
- Sophie Lissitzky-Küppers (ed.), El Lissitzky: Maler, Architekt, Typograf, Fotograf, Errinerungen, Briefe Schirften, Dresden: VEB Verlag der Kunst, 1967, 407 pp. (in German)
- El Lissitzky: Life, Letters, Texts, trans. Helene Aldwinckle, London: Thames and Hudson, 1968; 1980.
- Margarita Tupitsyn, El Lissitzky: Beyond the Abstract Cabinet: Photography, Design, Collaboration, New Haven/London: Yale University Press, 1999, 239 pp.
- El Lissitzky: Jenseits der Abstraktion, Fotografie, Design, Kooperation, Munich: Schimer/Mosel, 1999, 239 pp. (in German)
- Perloff, Nancy Lynn; Reed, Brian, eds. (2003). Situating El Lissitzky: Vitebsk, Berlin, Moscow. Getty Publications. Contents, [18]
- Nancy Perloff, "The Puzzle of El Lissitzky's Artistic Identity", pp 1-23.
- Christina Lodder, "El Lissitzky and the Export of Constructivism", pp 27-46.
- Éva Forgács, "Definitive Space: The Many Utopias of El Lissitzky's Proun Room", pp 47-75.
- Maria Gough, "Constructivism Disoriented: El Lissitzky's Dresden and Hannover Demonstrationsräume", pp 76-125.
- John E. Bowlt, "Manipulating Metaphors: El Lissitzky and the Crafted Hand", pp 129-152.
- Leah Dickerman, "El Lissitzky's Camera Corpus", pp 153-176.
- Margarita Tupitsyn, "After Vitebsk: El Lissitzky and Kazimir Malevich", 1924-1929, pp 177-195.
- T. J. Clark, "El Lissitzky in Vitebsk", pp 199-210.
- Peter Nisbet, "El Lissitzky circa 1935: Two Propaganda Projects Reconsidered", pp 211-234.
- El Lissitzky. Wolkenbügel 1924-1925, Madrid: Editorial Rueda, Madrid, 2005, 152 pp. (in English/Spanish) [19]
- Catalogues
- Franz Roh, Jan Tschichold (eds.), Foto-Auge / Oeil et Photo / Photo-Eye, Stuttgart: Akademischer Verlag Dr. Fritz Wedekind, 1929, 77 pp, 78 photographs. (in German, French and English). A photobook based on the Film und Foto exhibition organised by the Deutscher Werkbund in Stuttgart in 1929. The front-cover shows El Lissitzky's self-portrait (Küppers, plate 114). Includes works by Baumeister, Max Ernst, G. Grosz, Heartfield, Teige, Moholy-Nagy, Edward Weston, Peter Hans, Renger-Patzsch, Hans Leistikow, Willi Baumeister, Walter Funkat, Dsiga Wertoff. The book features various techniques of photography eg. photogram, x-rays-photo, photomontage. Designed by Jan Tschichold. [20] [21]
- El Lissitzky, Cologne: Galerie Gmurzynska, 1976.
- Nisbet, Peter, ed. (1987). El Lissitzky, 1890-1941. Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Art Museums, Busch-Reisinger Museum.
- El Lissitzky and Alexander Dorner: Kabinett der Abstrakten – Original and Facsimile, Berlin: Museum of American Art, 2009, 32 pp.
- Book chapters, Papers, Articles
- Ernő Kállai, "Lissitzky", Das Kunstblatt 6:1, 1922. Trans. Helene Aldwinckle and Mary Whittall, in Lissitzky: Life, Letters, Texts, 1980. [22]
- Ernő Kállai, "El Lissitzky", De Cicerone 6:22 (November 1922), pp 1058, 1063. Trans. Helene Aldwinckle and Mary Whittall, in Lissitzky: Life, Letters, Texts, 1980.
- Traugott Schakher, "El Lissitzky", Gebrauchsgraphik 5:12, 1928.
- Door van den Eeckhout, "Lissitzky's electro-mechanisch amphitheater", Elsevier 38:76, (July-December 1928). (in Dutch)
- Lucia Moholy, "El Lissitzky", The Burlington Magazine 108:756 (March 1966), pp 160-161+163.
- Alan C. Birnholz, "Notes on the Chronology of El Lissitzky's Proun Compositions", The Art Bulletin 55:3 (September 1973), pp 437-439
- Steven Mansbach, Visons of Totality: Laszlo Moholy-Nagy, Theo Van Doesburg, and El Lissitzky, University of Michigan Press, 1978.
- Yve-Alain Bois, Christian Hubert, "El Lissitzky: Reading Lessons", October, Vol. 11, Essays in Honor of Jay Leyda (Winter 1979), pp 113-128.
- Lynn Gumpert, "El Lissitzky's Proun I. Kestnermappe", Bulletin, Vol. 2, 1979, pp 56-69. [23]
- Benjamin H. D. Buchloh, "From Faktura to Factography", October, Vol. 30 (Autumn 1984), pp 82-119.
- Esther Levinger, "El Lissitzky's art-games", Neohelicon 14:1, 1987, pp 177-191. [24]
- Esther Levinger, "Art and Mathematics in the Thought of El Lissitzky: His Relationship to Suprematism and Constructivism", Leonardo 22:2 (1989), pp 227-236.
- Manuel Corrada, "On Some Vistas Disclosed by Mathematics to the Russian Avant-Garde: Geometry, El Lissitzky and Gabo", Leonardo 25:3/4, Visual Mathematics: Special Double Issue (1992), pp 377-384.
- Victor Margolin, The Struggle for Utopia: Rodchenko, Lissitzky, Moholy-Nagy, 1917-1946, University of Chicago Press, 1998. [25]
- Paul Galvez, "Self-Portrait of the Artist as a Monkey-Hand", October 93, 2000.
- Igor Dukhan, "El Lissitzky: Jewish as Universal: From Jewish Style to Pangeometry", Ars Judaica, 2007, pp 1-20.
- Alexandra Shatskikh, Vitebsk: The Life of Art, Yale University Press, 2007.
- Seth L. Wolitz, "El Lissitzky", The Yivo Encyclopedia of Jews in Eastern Europe, c2010.
- John G. Hatch, "Some Adaptations of Relativity in the 1920s and the Birth of Abstract Architecture", Nexus Network Journal 12:1, 2010, pp 131–147.
- Maria Gough, "Contains Graphic Material: El Lissitzky and the Topography of G", in G: An Avant-Garde Journal of Art, Architecture, Design, and Film, 1923-1926, eds. Detlef Mertins and Michael William Jennings, Getty Publications, 2010, pp 21-52.
- Maria Gough, "The Abstract Environment", in Inventing Abstraction, 1910-1925: How a Radical Idea Changed Modern Art, eds. Leah Dickerman and Matthew Affron, New York: Museum of Modern Art, 2012, pp 310-323. [26]
- Theses
- Alan C. Birnholz, El Lissitzky, Yale University, 1973. Ph.D. dissertation.
- Peter Nisbet, El Lissitzky in the Proun Years: A Study of His Work and Thought, 1917–1927, Yale University, 1995, 599 pp. Ph.D. dissertation. [27]
- Kemal Reha Kavas, Architectural Form Generation in Suprematist Painterly Space: The Significance of El Lissitzky's Prouns, Middle East Technical University, 2005, 120 pp. Master Thesis.
- Fabian Ziegler, El Lissitzky - Proun. Zur Logik der Form, Vienna: Vienna University, 2010, 132 pp. Master thesis. (in German)
- Film
See also
- Sophie Lissitzky-Küppers
- Suprematism
- Russia#Avant-garde
- Central and Eastern Europe#Constructivists, Futurists
External links
- "Monuments of the Future": Designs by El Lissitzky (Getty Research Institute)
- Lissitzky's profile at Van Abbe Museum (in Dutch)
- Lissitzky at Beinecke Rare Book & Manuscript Library
- Lissitzky at Google Art Project
- Lissitzky at The International Chamber of Russian Modernism, InCoRM (Patricia Railing)
- A selection of works by Lissitzky
- Lissitzky at Avantgardism.ru
- About 2 Squares by Lissitzky, 1922. [30]
- Models of Lissitzky's reconstructions of Malevich's figures from the Victory Over the Sun opera by Henry Milner, 2009.
- On Lissitzky's design for a yacht club on Lenin Hills, 1925.
- Lissitzky's Pelikan designs
- Lissitzky at Wikipedia
- Kabinett der Abstrakten at German Wikipedia
- Lissitzky on Facebook