Lisa Blackman: Loving the Alien: A Post-Post-Human Manifesto (2016)
Filed under booklet | Tags: · alien, body, human, manifesto, politics, posthumanism, subjectivation, subjectivity

This essay explores the ambivalent position of the alien in order to reflect upon the question of whether there is a place for a non-body politic. Lisa Blackman brings together a number of different debates from “new biologies” to “alien phenomenologies” that provide some ways of framing a possible non-body politics founded on radical relationality, contingency and “inhuman formation” that might go some small way to recognising what might be at stake.
Publisher Fall Semester, Miami, 2016
Open access
22 pages
via Fall Semester
PDF, PDF
Later version, published in Subjectivity, Apr 2017: HTML, PDF
Glossary of Common Knowledge (2017)
Filed under book | Tags: · art theory, commons, contemporary art, geopolitics, glossary, history, politics, subjectivation, subjectivity, theory
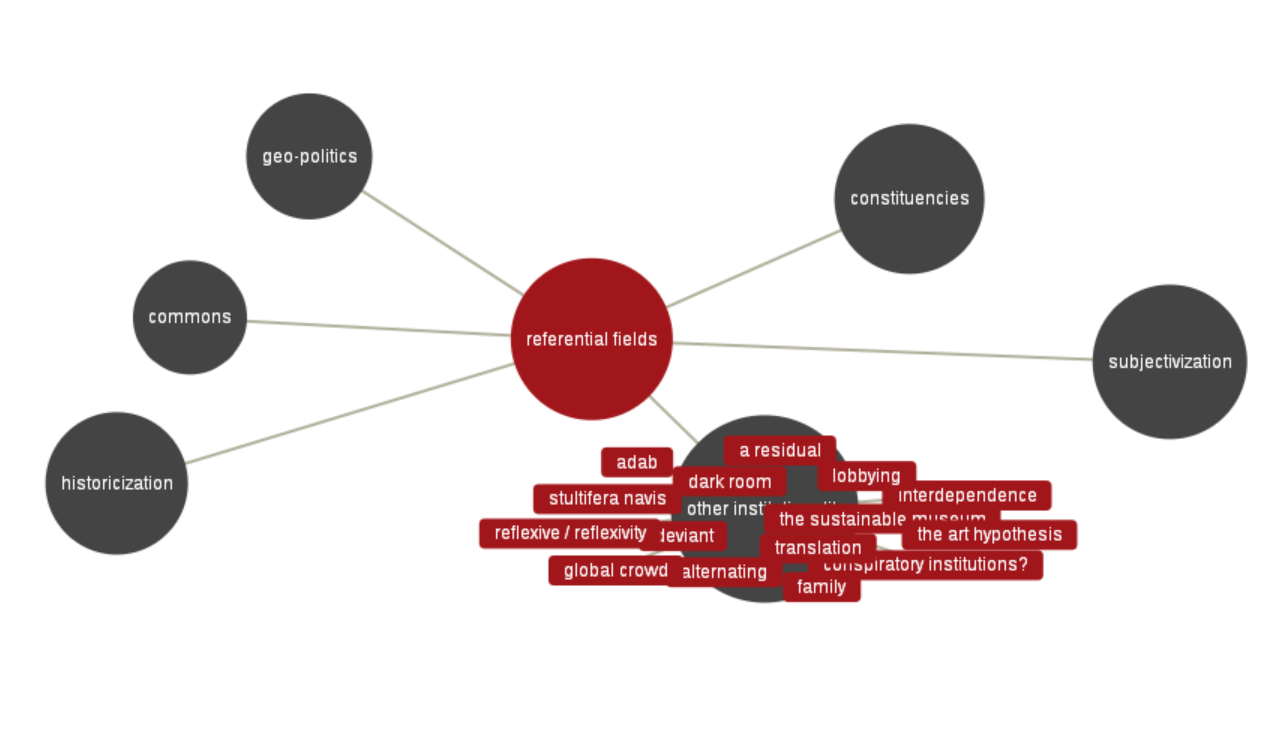
The Glossary of Common Knowledge is a research project by MG+MSUM, Ljubljana, in the frame of L’Internationale, aiming to negotiate various positions, contexts and local narratives about contemporary art. The glossary entries were produced through six seminars (2014-17), each focusing on one selected referential field: historicization, subjectivization, geo-politics, other institutionality, and commons. The resulting website now functions as an open platform accepting new contributions.
Fields and terms:
Historicization: archive, constellation, emancipation, temporally embodied sound, estrangement, heterochronia, humanism, intuition, pathological fracture, phantom (pain), reconstruction, self-historicization, temporalities, tendencies in art, the contemporary.
Subjectivization: creleasure, dancing as insurrectional practice, decolonize, evidence, fragility, interest, kapwa, loser, over-identification, radical imagination, self-determination, self-representation, on subjectivization, the subject, travesti, unrest.
Geo-politics: agitational visual language, alignment, catastrophe, eurasia, event, global resistance, institutional geopolitical strategies, migrancy, non-aligned movement, pandemic, postsocialism, south, tudigong, god of the land, white space.
Constituencies: agency, autonomy, biotope, bureaucratisation, collaboration / co-labour, construction, the continuity-form and counter-continuity, de-professionalization, intervenor, labour, ñande / ore, the eternal network / la fête permanente, the rest is missing.
Commons: to baffle, basic income, the brotherhood & unity highway, constituent power of the common, corrected slogan, data asymmetry , friendship, heterotopian homonymy, institution, noosphere, palimpsest, rog, self-management, solidarity, theft.
Other institutionality: a residual, adab, alternating, conspiratory institutions?, dark room, deviant, family, global crowd, interdependence, lobbying, reflexive / reflexivity, stultifera navis, the sustainable museum, the art hypothesis, translation.
Curated by Zdenka Badovinac, Bojana Piškur and Jesús Carrillo (MNCARS) in collaboration with L’Internationale, et al
Publisher MG+MSUM, Ljubljana, 2017
HTML (on the website of MG+MSUM)
HTML (on the website of L’Internationale, added on 2020-4-12)
Seminar recordings structured by terms discussed
October, 155: A Questionnaire on Materialisms (2016)
Filed under survey | Tags: · actor-network theory, anthropocene, art, human, materialism, networks, object-oriented ontology, philosophy, speculative realism, subject, subjectivity, thing
“Recent philosophical tendencies of “Actor-Network Theory,” “Thing Theory,” “Object-Oriented Ontology,” “Speculative Realism,”and “Vibrant Materialism,” have profoundly challenged the centrality of subjectivity in the humanities and, arguably, the perspectives that theories of the subject from the psychoanalytic to the Foucauldian have afforded (on the operations of power, the production of difference, and the constitution of the social, for instance). At least four moves characterize these discourses:
• Attempting to think the reality of objects beyond human meanings and uses. This other reality is often rooted in “thingness” or an animate materiality.
• Asserting that humans and objects form networks or assemblages across which agency and even consciousness are distributed.
• Shifting from epistemology, in all of its relation to critique, to ontology, where the being of things is valued alongside that of persons.
• Situating modernity in geological time with the concept of the “Anthropocene,” an era defined by the destructive ecological effects of human industry.
Many artists and curators, particularly in the UK, Germany, and the United States, appear deeply influenced by this shift. Is it possible, or desirable, to decenter the human in discourse on art in particular? What is gained in the attempt, and what—or who—disappears from view? Is human difference—gender, race, power of all kinds—elided? What are the risks in assigning agency to objects; does it absolve us of responsibility, or offer a new platform for politics?” (from the introduction)
Responses by Emily Apter, Ed Atkins, Armen Avanessian, Bill Brown, Giuliana Bruno, Julia Bryan-Wilson, D. Graham Burnett, Mel Y. Chen, Andrew Cole, Christoph Cox, Suhail Malik, T. J. Demos, Jeff Dolven, David T. Doris, Helmut Draxler, Patricia Falguières, Peter Galison, Alexander R. Galloway, Rachel Haidu, Graham Harman, Camille Henrot, Brooke Holmes, Tim Ingold, Caroline A. Jones, Alex Kitnick, Sam Lewitt, Helen Molesworth, Alexander Nemerov, Michael Newman, Spyros Papapetros, Susanne Pfeffer, Gregor Quack, Charles Ray, Matthew Ritchie, André Rottmann, Amie Siegel, Kerstin Stakemeier, Artie Vierkant, McKenzie Wark, Eyal Weizman, Christopher S. Wood, and Zhang Ga.
Edited by David Joselit, Carrie Lambert-Beatty, and Hal Foster
Publisher MIT Press, Winter 2016
ISSN 0162-2870
108 pages
PDF (updated on 2017-11-24)
Comment (0)
