Coronavirus and Philosophers (2020) [IT, EN, ES]
Filed under dossier | Tags: · biology, biopolitics, community, contagion, democracy, pandemic, philosophy, politics, quarantine, state of exception, virus
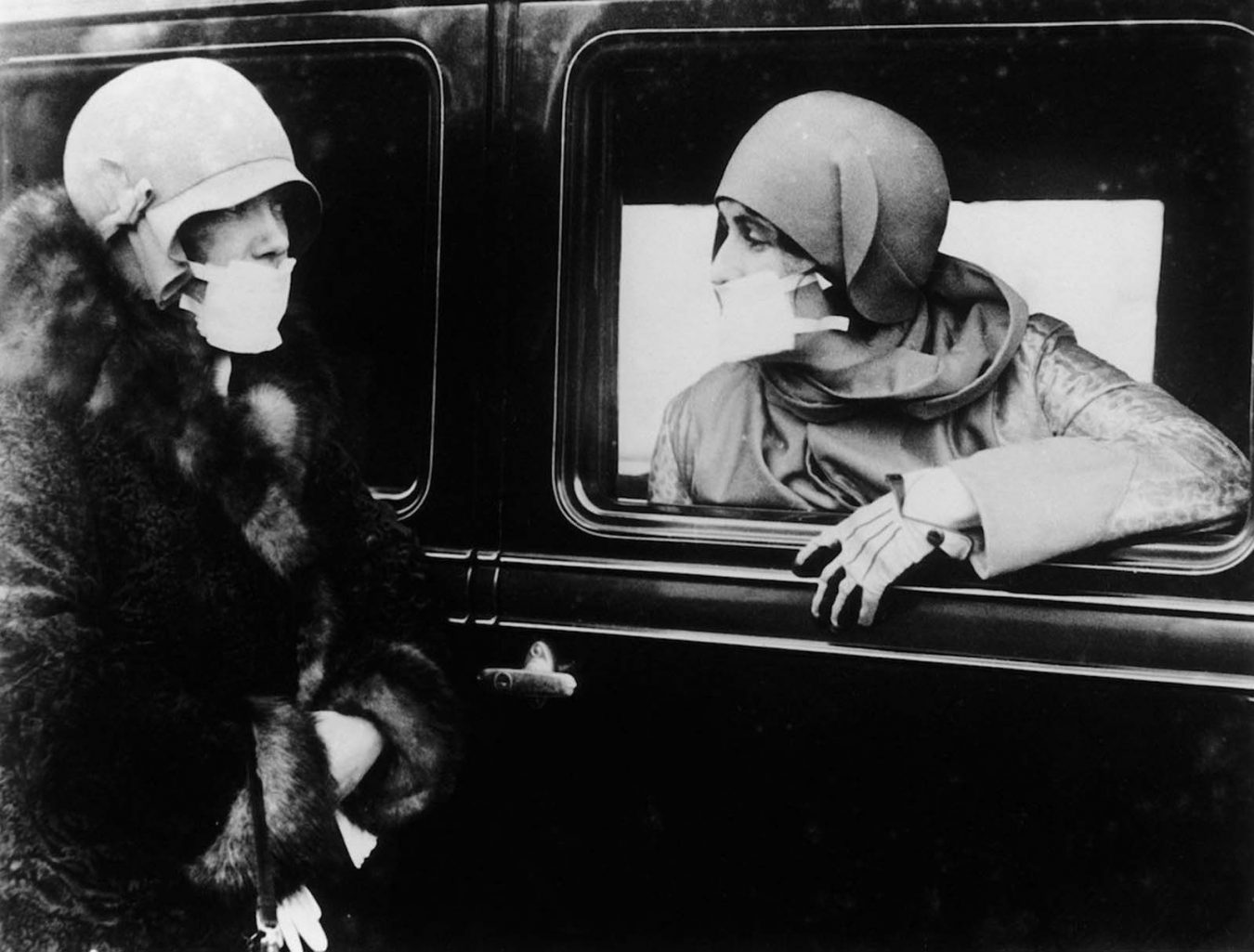

Debate on the current Coronavirus (COVID-19) events and the state of exception sparkled by Giorgio Agamben’s article with contributions from Jean-Luc Nancy, Roberto Esposito, Sergio Benvenuto, Divya Dwivedi, Shaj Mohan, Rocco Ronchi, Massimo de Carolis, and others, in the Italian journal Antinomie. Included is an excerpt from Michel Foucault’s Discipline and Punish on the measures taken in the wake of a plague in the 17th century.
English translations of selected texts have been published by the European Journal of Psychoanalysis.
An expanded edition in Spanish was edited by Pablo Amadeo and published by ASPO (Aislamiento Social Preventivo y Obligatorio).
Paradoxia epidemica (Italian, HTML)
Coronavirus and Philosophers (English, Mar 2020, HTML, subsequent texts)
Sopa de Wuhan (Spanish, 29 Mar 2020, PDF, added on 2020-4-18)
Technosphere Magazine: Materials (2018)
Filed under dossier, magazine | Tags: · anthropocene, materials, matter, technosphere
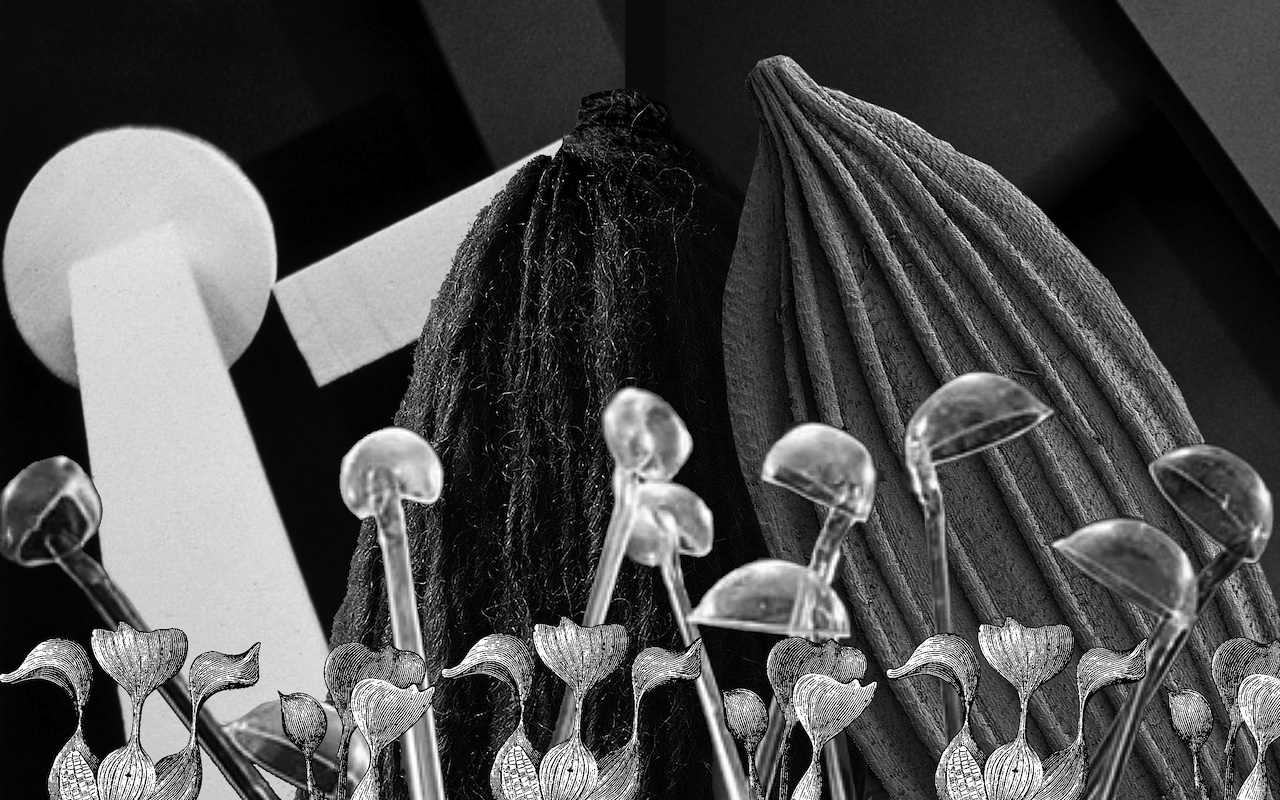

“Stuff matters. In much of history, the real protagonists were the precious metals, burning hydrocarbons, superior aerogels, collapsing concrete, rare minerals, and toxic liquids. This goes for all chemical compounds, whether raw, processed, or newly designed, geogenic, biogenic, or anthropogenic. It is the inventory and also the political, ecologic, and economic criticality of the material world within which humans will always have to situate themselves. Inert matter constitutes the raw materials of life, while organic matter changes the chemical composition of other spheres, such as the atmosphere or the lithosphere. This is what Vladimir Vernadsky and others have taught us. Yet this eons-old circulation of matter has been perturbed, on a grand scale, by the intervention of a new sphere: the technosphere.
Perhaps the largest achievement in modern science is the studying of the properties of materials. In doing so, humans have discovered tools that have reshaped the world to the extent that the Earth has intractably reformulated itself in marked contrast from its prehuman trajectories. The whole technosphere rests on the mobilization and organization of (energetic) matter: its extraction, cracking, transformation, manipulation, and finally, dispersion. As a result, the entire material world has been turned into a resource to be manipulated, consumed, or reordered. It is the industrialization of this relationship between humankind and all matter that has contributed decisively to creating the technosphere.
This dossier discusses the criticality of the material world as the spatiotemporal backbone of the technosphere and, eventually, ourselves. It presents stories of stuff, from mining to discarding, by dwelling on the pure substances themselves as well as their endless variety, but also by bringing the logistics and transversal interrelations between them into focus. It asks about the relationship of artifacts and craft, the blurring lines between naturalness and artificiality, and even what defines the line between living and dead material.”
With contributions by Annapurna Mamidipudi, Sophia Roosth, Nicole Koltick, Sander van der Leeuw & Daniel Niles, Elaine Gan, and Esther Leslie.
Publisher Haus der Kulturen der Welt (HKW), Berlin, March 2018
Open access
CCCBLab: The Future of the Book (2015)
Filed under dossier | Tags: · book, publishing, storytelling
“The literary and publishing ecosystem is facing a major transformation. Can we imagine a future beyond the traditional book? What’s going on with new readers, digital narratives and publishing options in a world that’s changing for good?”
With contributions by Jorge Carrión, Javier Celaya, Mariana Eguaras, Martín Gómez, Alessandro Ludovico, Carles Sora, and Jose Valenzuela Ruiz.
Publisher CCCB, Barcelona, 2015
Open access

