Limn, 0-2: Prototyping Prototyping / Systemic Risk / Crowds and Clouds (2010-2012)
Filed under magazine | Tags: · big data, cloud computing, crowdsourcing, data mining, economy, financial crisis, internet, networks, politics, social media, surveillance
Limn, 0: Prototyping Prototyping, Nov 2010
“Before there was LIMN, there were several different prototypes. The first was occasioned by a conference: on prototypes. Held in Madrid in November of 2010, and organized by Adolpho Estalella and Alberto Corsín Jimenez, it was a conference for which this issue was imagined as a kind of pre-conference publication–another riff on the prototype. Many of the problems LIMN seeks to address were worked out in part through this conference and the publication: from the use of new media, to the function of conferences and conference papers, to the idea of a publication that precedes or determines a social event. Issue Number Zero was very much a prototype, and bears the traces of that concept and the discussion of it by the generous participants.”
Contributors: George Marcus, Marilyn Strathern, James Leach, Alberto Corsin Jimenez and Adolfo Estalella, Alex Wilkie, Nerea Calvillo, Javier Lezaun, Lucy Suchman, Lina Dib, Michael Guggenheim, Alain Pottage
HTML (updated on 2019-7-8)
Limn, 1: Systemic Risk, Jan 2011
“Systemic risk has become a central topic of expert discussion and political debate amidst the financial crisis that began in 2008, but it also has resonances across many other domains in which catastrophic threats loom – including internet security, supply chain management, catastrophe insurance, and critical infrastructure protection. In this issue, we invited scholars to contribute genealogical and conceptual framings that inform critical inquiry into this increasingly important concept. The result is not a traditional collection of academic articles but a set of brief, preliminary reflections, prepared on short notice, that address a common set of questions, along with a handful of documents, links, images and videos that illustrate different aspects of the concept.”
Contributors: Benjamin Sims, Deborah Cowen, Myriam Dunn Cavelty, Elizabeth Cullen Dunn, Christopher M. Kelty, Philip Bougen, Stephen J. Collier, Andrew Lakoff, Onur Ozgöde, Douglas R. Holmes, Rebecca Lemov, Brian Lindseth, Martha Poon, Grahame Thompson
HTML (updated on 2019-7-8)

Limn, 2: Crowds and Clouds, Mar 2012
“This issue of LIMN focuses on new social media, data mining and surveillance, crowdsourcing, cloud computing, big data, and Internet revolutions. Rather than follow the well-worn paths of argument typical today, our contributors address the problems in new ways and at odd angles: from the power and politics of statistics and algorithms to crowdsourcing’s discontents to the capriciousness of collectives in an election; from the focus group and the casino to the worlds of micro-finance and data-intensive policing. Together they raise questions about the relationship of technology and the collectives that form in and through them.”
Contributors: Christopher Kelty, Alain Desrosières, Lilly Irani, Chris Csikszentmihályi, Gabriella Coleman, Nick Seaver, Emmanuel Didier, Alek Felstiner, Tarleton Gillespie, Roma Jhaveri, Daniel Kreiss, Natasha Dow Schüll, Rebecca Lemov, Maria Vidart, Amira Pettus, Jonathan R. Baldwin, and Ruben Hickman
HTML (updated on 2019-7-8)
“Limn is somewhere between a scholarly journal and an art magazine. It is an attempt to communicate and display ongoing scholarly research. Limn outlines contemporary problems. It draws material from networks of experts in the social and human sciences and is intended to be timely, diverse in perspective, authoritative, well written and beautifully designed. The focus is on contemporary problems in our global, politically interconnected, technologically intense culture: problems of infrastructure, ecological vulnerability, economic interdependence, and relentless technological invention.”
Editors: Stephen J. Collier, Christopher M. Kelty, Andrew Lakoff
Creative Commons BY-SA 3.0 Unported License
dj readies (Craig J. Saper): Intimate Bureaucracies: A Manifesto (2012)
Filed under book | Tags: · activism, bureaucracy, democracy, networks, occupy movement, politics

Intimate Bureaucracies is a history from the future looking backward at our present moment as a turning point. Our systems of organization and control appear unsustainable and brutal, and we are feeling around in the dark for alternatives. Using experiments in social organization in downtown New York City, and other models of potential alternative social organizations, this manifesto makes a call to action to study and build sociopoetic systems.
One alternative system, the Occupy movement, has demands and goals beyond the specific historical moment and concerns. This short book/manifesto suggests that the organization and communication systems of Occupying encampments represent important necessities, models, goals, and demands, as well as an intimate bureaucracy that is a paradoxical mix of artisanal production, mass-distribution techniques, and a belief in the democratizing potential of social media.
Participatory decentralization, a mantra of political networks, expresses a peculiar intimate bureaucratic form. These forms of organization represent a paradoxical mix of artisanal production, mass-distribution techniques, and a belief in the democratizing potential of social media. Borrowing from mass-culture image banks, these intimate bureaucracies play on forms of publicity common in societies of spectacles and public relations. Intimate bureaucracies monitor the pulse of the society of the spectacle and the corporatized bureaucracies: economics as in Big Business, culture as in Museums and Art Markets, mass media as in Studio Systems and Telecommunication Networks, safety as in Big Brother militarized police forces, and politics as in Big Government. Rather than simply mounting a campaign against big conglomerations of business, government, police, and culture, these intimate bureaucracies and their works use the forms of corporate bureaucracies for intimate ends. Rather than reach the lowest common denominator, they seek to construct what those in the business world would call niche marketing to ultra-specific demographics. Businesses, interested in utilizing the World Wide Web and the Internet, already use these strategies for niche marketing. The historical examples and sketches, explored in this pamphlet, examine how these cultural experiments emulate and resist the systems used in Internet marketing.
The apparent oxymoron, intimate bureaucracies, suggests not only a strategy, but the very basis for the new productive mythology surrounding the electronic World Wide Web.
Intimacy, the close familiarity of friendship or love, by definition depends on a small-scale system of communication. Its warmth, face-to-face contact, and fleeting impact has often made it the subject of art and literature. It usually only appears in administration situations as either an insincere ornamentation of a political campaign (“pressing the flesh” or “kissing babies”), or as inappropriate office behavior (affairs, gossip, child abuse, etc.), but rarely as the center of a political system. The “small is beautiful” movement of the 1960’s and 1970’s did suggest the possibility of an intimacy in politics, but not how to scale the system to the size of a government.
Publisher Punctum Books, Brooklyn, New York; with AK Press Tactical Media, Baltimore / Oakland / Edinburgh; and Minor Compositions, Wivenhoe / Brooklyn / Port Watson, March 2012
ISBN 978-0615612034
Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommerical-NoDerivs 3.0 Unported License
60 pages
Mapping the Arabic Blogosphere: Politics, Culture and Dissent (2009)
Filed under report | Tags: · blogging, culture, egypt, human rights, internet, islam, middle east, networks, politics, religion
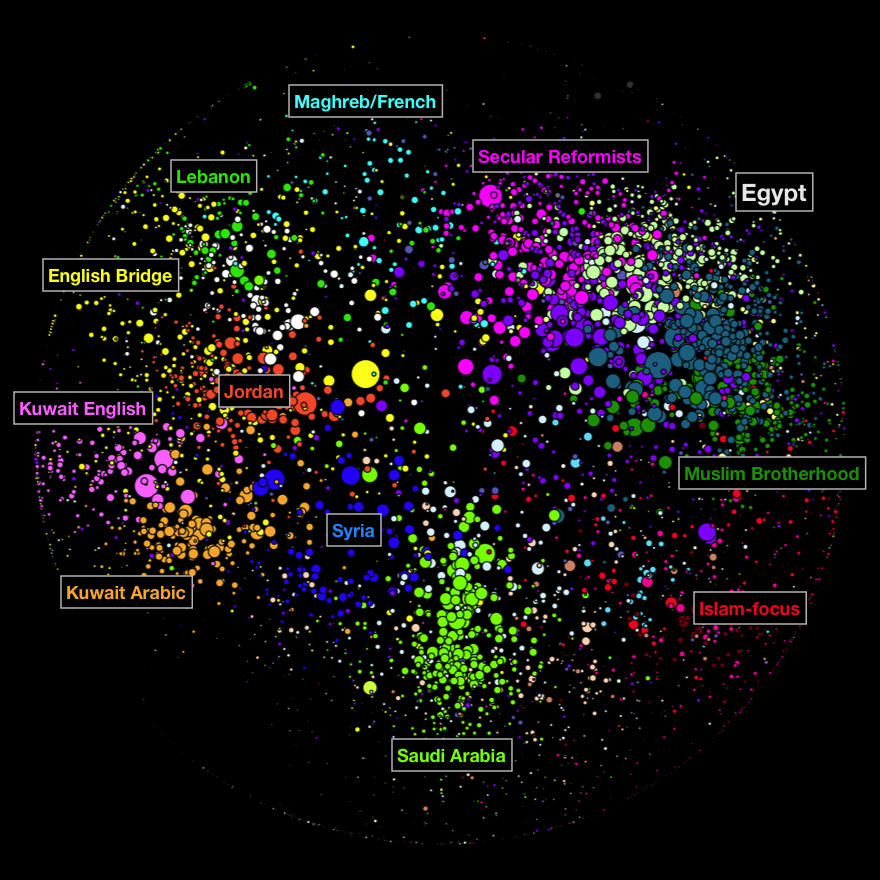
“We conducted a study of the Arabic language blogosphere using link analysis, term frequency analysis, and human coding of individual blogs. We identified a base network of approximately 35,000 active blogs, created a network map of the 6,000 most connected blogs, and with a team of Arabic speakers hand coded 4,000 blogs. The goal for the study was to produce a baseline assessment of the networked public sphere in the Arab Middle East, and its relationship to a range of emergent issues, including politics, media, religion, culture, and international affairs.”
Authored by Bruce Etling, John Kelly, Rob Faris, John Palfrey, Internet and Democracy
Published by Berkman Center, June 2009
Internet & Democracy Case Study Series
Berkman Center Research Publication No. 2009-06
62 pages