La Société Anonyme: The SKOR Codex (2012)
Filed under artist publishing | Tags: · archive, archiving, art, code, data, digital heritage, media art, preservation, print, storage
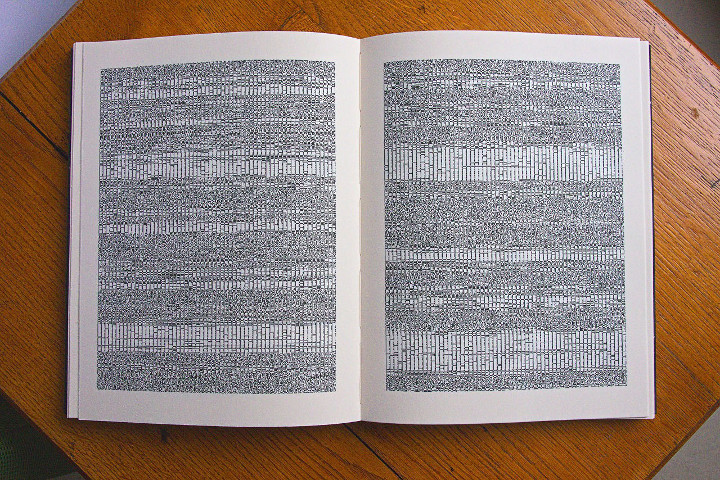
The SKOR Codex is a printed book which will be sent to different locations on earth. It contains binary encoded image and sound files selected to portray the diversity of life and culture at the Foundation for Art and Public Domain (SKOR), Amsterdam, and is intended for any intelligent terrestrial life form, or for future humans, who may find it. The files are protected from bitrot, software decay and hardware failure via a transformation from magnetic transitions on a disk to ink on paper, safe for centuries. Instructions in a symbolic language explain the origin of the book and indicate how the content is to be decoded.
La Société Anonyme noted that “the package will be encountered and the book decoded only if there will be advanced civilizations on earth in the far future. But the launching of this ‘bottle’ into the cosmic ‘ocean’ says something very hopeful about art on this planet.” Thus the record is best seen as a time capsule and a statement rather than an attempt to preserve SKOR for future art historians. The SKOR Codex is a project by La Société Anonyme.
Published in July 2012
304 pages
Interview with authors (Annet Dekker, Open!, 2014).
Comment (0)David M. Berry (ed.): Life in Code and Software: Mediated Life in a Complex Computational Ecology (2012)
Filed under living book | Tags: · code, computing, life, media ecology, media literacy, software

The essays in this collection, edited by David M. Berry, Senior Lecturer in Digital Media in the Department of Political and Cultural Studies at Swansea University, explore the relationship between living, code and software. For Berry, technologies of code and software increasingly make up an important part of our urban environment – indeed, their reach stretches to even quite remote areas of the world. Life in Code and Software introduces and explores the way in which code and software are becoming the conditions of possibility for human living, crucially forming a computational ecology, made up of disparate software ecologies we inhabit. As such we need to take account of this new computational environment, Berry argues, and think about how today we live in a highly mediated, code-based world – a world where computational concepts and ideas are foundational, and within which, code and software become the paradigmatic forms of knowing and doing.
Publisher Open Humanities Press, July 2012
Living Books About Life series
ISBN 9781607852834
View online (wiki/PDF/HTML articles/videos)
PDF (PDF’d Introduction with hyperlinked articles)
George Dyson: Turing’s Cathedral: The Origins of the Digital Universe (2012)
Filed under book | Tags: · code, computing, history of computing, turing machine

“It is possible to invent a single machine which can be used to compute any computable sequence,” twenty-four-year-old Alan Turing announced in 1936. In Turing’s Cathedral, George Dyson focuses on a small group of men and women, led by John von Neumann at the Institute for Advanced Study in Princeton, New Jersey, who built one of the first computers to realize Alan Turing’s vision of a Universal Machine. Their work would break the distinction between numbers that mean things and numbers that do things—and our universe would never be the same.
Using five kilobytes of memory (the amount allocated to displaying the cursor on a computer desktop of today), they achieved unprecedented success in both weather prediction and nuclear weapons design, while tackling, in their spare time, problems ranging from the evolution of viruses to the evolution of stars.
Dyson’s account, both historic and prophetic, sheds important new light on how the digital universe exploded in the aftermath of World War II. The proliferation of both codes and machines was paralleled by two historic developments: the decoding of self-replicating sequences in biology and the invention of the hydrogen bomb. It’s no coincidence that the most destructive and the most constructive of human inventions appeared at exactly the same time.
How did code take over the world? In retracing how Alan Turing’s one-dimensional model became John von Neumann’s two-dimensional implementation, Turing’s Cathedral offers a series of provocative suggestions as to where the digital universe, now fully three-dimensional, may be heading next.
Publisher Knopf Doubleday Publishing Group, 2012
ISBN 0307907066, 9780307907066
432 pages
review (Edward J. Valauskas, First Monday)
review (Francis Spufford, The Guardian)
review (William Poundstone, The New York Times)
review (Robert Barry, review31)

