Bruno Jasieński: I Burn Paris (1928–) [PL, EN, ES]
Filed under fiction | Tags: · avant-garde, catastrophe, communism, futurism, marxism

I Burn Paris has remained one of Poland’s most uncomfortable masterstrokes of literature since its initial and controversial serialization by Henri Barbusse in 1928 in L’Humanité (for which Jasieński was deported for disseminating subversive literature). It tells the story of a disgruntled factory worker who, finding himself on the streets, takes the opportunity to poison Paris’s water supply. With the deaths piling up, we encounter Chinese communists, rabbis, disillusioned scientists, embittered Russian émigrés, French communards and royalists, American millionaires and a host of others as the city sections off into ethnic enclaves and everyone plots their route of escape. At the heart of the cosmopolitan city is a deep-rooted xenophobia and hatred — the one thread that binds all these groups together. As Paris is brought to ruin, Jasienski issues a rallying cry to the downtrodden of the world, mixing strains of “The Internationale” with a broadcast of popular music.
With its montage strategies reminiscent of early avant-garde cinema and fist-to-the-gut metaphors, I Burn Paris has lost none of its vitality and vigor. Ruthlessly dissecting various utopian fantasies, Jasienski is out to disorient, and he has a seemingly limitless ability to transform the Parisian landscape into the product of disease-addled minds. An exquisite example of literary Futurism and Catastrophism, the novel presents a filthy, degenerated world where factories and machines have replaced the human and economic relationships have turned just about everyone into a prostitute. Yet rather than cliché and simplistic propaganda, there is an immediacy to the writing, and the modern metropolis is starkly depicted as only superficially cosmopolitan, as hostile and animalistic at its core.
This English translation of I Burn Paris fills a major gap in the availability of works from the interwar Polish avant-garde, an artistic phenomenon receiving growing attention with recent publications such as Caviar and Ashes.
First serialized in French as “Je brûle Paris” in L’Humanité in 1928.
Polish edition
Publisher Towarzystwo Wydawnicze “Rój”, Warsaw, 1929
English edition
Translated by Soren A. Gauger and Marcin Piekoszewski
With an Afterword by Soren Gauger
Publisher Twisted Spoon Press, Prague, 2012
ISBN 9788086264370
309 pages
Review (Benjamin Noys, Mute)
Review (M.A.Orthofer, The Complete Review)
Review (Isla Badenoch, Article Magazine)
Commentary (Nina Kolesnikoff, 1982)
Wikipedia (in Polish)
Publisher (EN)
Google books (EN)
Palę Paryż (Polish, 1929, HTML), Alt link
I Burn Paris (English, 2012, EPUB, removed on 2015-1-15 upon request of the publisher)
Anatol Stern’s 1957 preface (Polish), English translation (Issuu.com)
Voy a meterle fuego a París (Spanish, trans. Jorge Segovia and Violetta Beck, 2013, added on 2014-2-2)
Der Sturm (1910–1932) [German]
Filed under magazine | Tags: · abstract art, art, art criticism, art theory, avant-garde, constructivism, cubism, expressionism
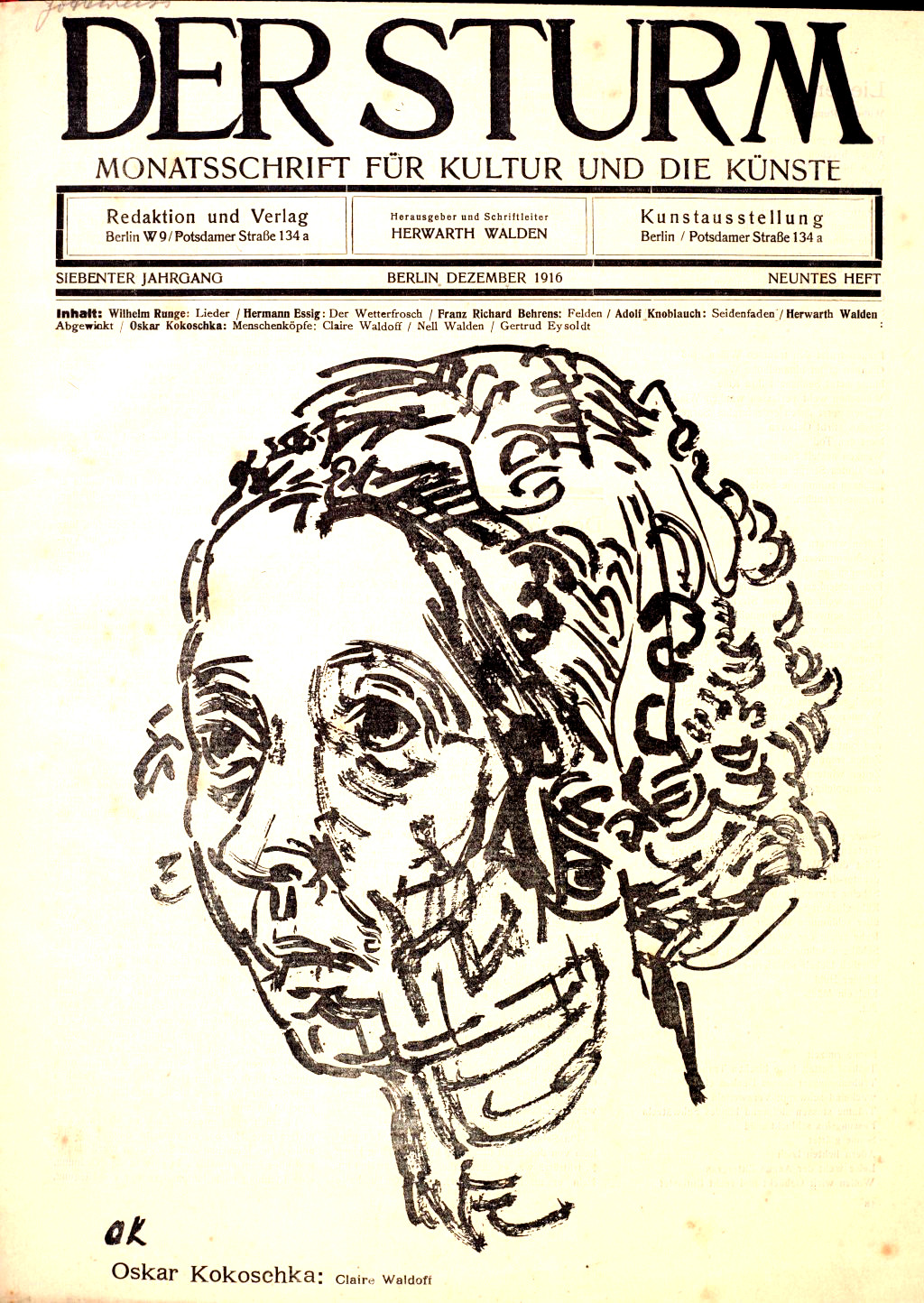


Der Sturm [The Storm] was a magazine covering the expressionism movement founded in Berlin in 1910 by Herwarth Walden. It ran weekly until monthly in 1914, and became a quarterly in 1924 until it ceased publication in 1932.
Among the literary contributors were Peter Altenberg, Max Brod, Richard Dehmel, Alfred Döblin, Anatole France, Knut Hamsun, Arno Holz, Karl Kraus, Selma Lagerlöf, Adolf Loos, Heinrich Mann, Paul Scheerbart, and René Schickele. Der Sturm consisted of pieces such as expressionistic dramas (i.e. from Hermann Essig and August Stramm), artistic portfolios (Oskar Kokoschka), essays from artists (the Kandinsky Album), and theoretical writings on art from Herwarth Walden. The term Sturm was branded by Walden to represent the way in which modern art was penetrating Germany at the time. (from Wikipedia)
View online (all 336 issues with a full-text search, at the Princeton University’s Blue Mountain Project)
Comment (0)Karl Toepfer: Empire of Ecstasy: Nudity and Movement in German Body Culture, 1910-1935 (1997)
Filed under book | Tags: · 1910s, 1920s, 1930s, avant-garde, ballet, bauhaus, body, dance, expressionism, germany, photography, theatre, weimar republic

Empire of Ecstasy offers an interpretation of the explosion of German body culture between the two wars—nudism and nude dancing, gymnastics and dance training, dance photography and criticism, and diverse genres of performance from solo dancing to mass movement choirs. Karl Toepfer presents this dynamic subject as a vital and historically unique construction of “modern identity.”
The modern body, radiating freedom and power, appeared to Weimar artists and intelligentsia to be the source of a transgressive energy, as well as the sign and manifestation of powerful, mysterious “inner” conditions. Toepfer shows how this view of the modern body sought to extend the aesthetic experience beyond the boundaries imposed by rationalized life and to transcend these limits in search of ecstasy. With the help of much unpublished or long-forgotten archival material (including many little-known photographs), he investigates the process of constructing an “empire” of appropriative impulses toward ecstasy.
Toepfer presents the work of such well-known figures as Rudolf Laban, Mary Wigman, and Oskar Schlemmer, along with less-known but equally fascinating body culture practitioners. His book is certain to become required reading for historians of dance, body culture, and modernism.
Publisher University of California Press, 1997
ISBN 0520918274, 9780520918276
422 pages
PDF’d HTML, HTML (from the publisher)
See also Mel Gordon, Voluptuous Panic: The Erotic World of Weimar Berlin, 2000–.
Comment (0)
