Charles W. Turner: Xenakis in America (2014)
Filed under book | Tags: · biography, composition, computer music, electroacoustic music, electronic music, mathematics, music, sound synthesis

Iannis Xenakis had a long-standing interest in the U.S., but given the five years he spent there, little has been written about his experiences. This study attempts, through archival research and interviews, to document Xenakis’ time in the United States. Its subject is his relationship to American cultural institutions, and the attraction of America for his musical composition and research.
Xenakis in America treats the period from Copland’s invitation to Tanglewood in 1963, through Xenakis’ 1972 investment by France as a state-supported artist. While he visited the U.S. many times thereafter, he no longer sought long-term engagement with U.S. institutions, but presented work completed elsewhere. After his summer at Tanglewood, performances of Xenakis compositions by Schuller, Foss and Bernstein (among others) are tracked throughout the 1960s and 1970s. Xenakis’ association with George Balanchine is examined, along with the reception of Xenakis’ theoretical writings, culminating in the publication of Formalized Music. in 1971. Xenakis’ collaboration with Alexis Solomos on Aeschylus’ Oresteia, produced in 1966 by the Ypsilanti Greek Theatre, is explored, as well as the founding of Xenakis’ research center CMAM at Indiana University in 1967, which he would build over the next five years.
Concerning Xenakis’ reasons for coming to America, there are two major motivations. First, there were reasons to look beyond France: its state institutions, up to the late 1960s, provided little support for avant-garde composition. Later, there were reasons to return: with the Polytope de Cluny of 1972, the Ministry of Culture signaled a policy change that favored Xenakis, and established his CeMAMu as a state-supported research center. Second, Xenakis’ opportunities in the U.S. satisfied his interest in working outside the boundaries of autonomous composition. The collaboration on the Ypsilanti Oresteia offered Xenakis involvement with both ancient and modern Greek theater, and Bloomington’s sponsorship of CMAM, which included the equipment necessary for computer synthesis of sound, gave Xenakis access to technology unavailable in France at the time.
Publisher One Block Avenue, Tappan/NY, October 2014
Open Access
ISBN 9780692267165
146 pages
The printed book is available from Lulu.com. Proceeds go to The Friends of Xenakis Association.
Comment (1)Jean-Luc Chabert, et al.: A History of Algorithms: From the Pebble to the Microchip (1994–) [French, English]
Filed under book | Tags: · algorithm, computing, history of computing, history of mathematics, mathematics, turing machine

A source book for the history of mathematics, but one which offers a different perspective by focusing on algorithms. With the development of computing has come an awakening of interest in algorithms. Often neglegted by historians and modern scientists, more concerned with the nature of concepts, algorithmic procedures turn out to have been instrumental in the development of fundamental ideas: practice led to theory just as much as the other way round. The purpose of this book is to offer a historical background to contemporary algorithmic practice. Each chapter centres around a theme, more or less in chronological order, and the story is told through the reading of over 200 original texts, faithfully reproduced. This provides an opportunity for the reader to sit alongside such mathematicians as Archimedes, Omar Khayyam, Newton, Euler and Gauss as they explain their techniques. The book ends with an account of the development of the modern concept of algorithm.
With Évelyne Barbin, Michel Guillemot, Anne Michel-Pajus, Jacques Borowczyk, Ahmed Djebbar, and Jean-Claude Martzloff
Publisher Belin, Paris, 1994
ISBN 2701113466, 9782701113463
591 pages
English edition
Translated by Chris Weeks
Publisher Springer, 1999
ISBN 3540633693
524 pages
Publisher (FR, new edition)
Publisher (EN)
Histoire d’algorithmes: du caillou à la puce (French, DJVU, 10 MB)
A History of Algorithms: From the Pebble to the Microchip (English, DJVU, 6 MB)
See also Algomation.com, a platform for viewing, creating and sharing algorithms.
Comment (0)The Optics of Ibn Al-Haytham, Books I–III: On Direct Vision (c1028-38/1989)
Filed under book | Tags: · colour, geometry, light, mathematics, optics, perception, physics, vision
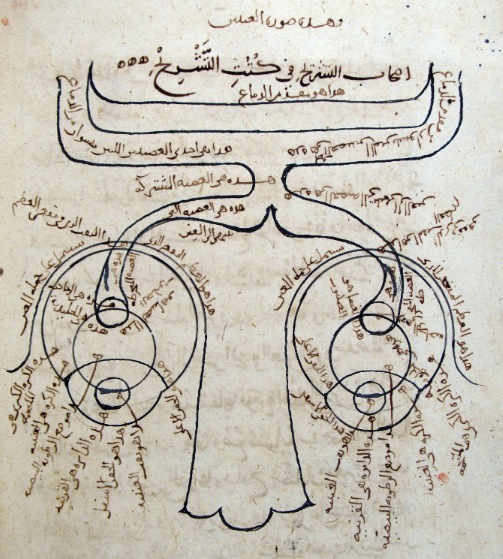
This is the first English translation of first three out of the 7 volumes of the fundamental work on optics by the medieval Arab scientist Ibn al-Haitham or Alhazen (965–c1039). His book exerted a great influence upon science through Witelo, Roger Bacon, Peckham and Kepler. Alhazen investigated many particular cases of reflection and refraction, and drew attention to the light-ray’s property of retracing its path when reversed. He was the first to give a detailed description of the human eye and to study binocular vision. Certain ophthalmological terms originated from the Latin translation of Alhazen’s Arabic text, e.g. retina and cornea.
The Book of Optics (Kitāb al-Manāẓir, كتاب المناظر) presented experimentally founded arguments against the widely held extramission theory of vision (as held by Euclid in his Optica) and in favour of intromission theory, as supported by thinkers such as Aristotle, the now accepted model that vision takes place by light entering the eye.
Part 1 contains the translation; Part 2 an introduction, commentary, Arabic-Latin glossaries, concordance, bibliography, and indices.
Edition of the Arabic text, edited by A. I. Sabra, was published by National Council for Culture, Arts and Letters, Kuwait, in 1983 (Books I-III) and 2002 (Books IV-V). Sabra’s translation of the latter has not yet been published.
Translated with Introduction and Commentary by A. I. Sabra
Publisher The Warburg Institute, University of London, London, 1989
Studies of the Warburg Institute, 40/1-2
ISBN 0854810722, 9780854810727
367 and 246 pages, 4 plates (following p. 42 in Part 2)
Review (Alexander Jones, Isis, 1991)
Review (George Saliba, Speculum, 1992)
Wikipedia
Translator
Publisher (WI)
Publisher (SAS)
PDF (pp xvi-xix of Part 2 missing; 18 MB)
Latin translation:
Liber de aspectiibus et vocatur prospectiva (digital facsimile of Latin translation of all 7 volumes, manuscript, Ms 1393)
Opticae thesaurus (edition of the Latin translation by Friedrich Risner, 1572; Archive.org)
See also the first episode of Simon Schaeffer’s 2004 BBC documentary series Light Fantastic, “Let There Be Light”, where he discusses Alhazen and others.
Comment (0)
