Trevor Pinch, Karin Bijsterveld (eds.): The Oxford Handbook of Sound Studies (2011)
Filed under book | Tags: · acoustics, computing, data visualisation, electronic music, field recording, game studies, hip hop, listening, medicine, music, noise, perception, phonograph, radio, science, sonification, sound, sound design, sound recording, sound studies, vision

“Written by the leading scholars and researchers in the emerging field of sound studies, The Oxford Handbook of Sound Studies offers new and fully engaging perspectives on the significance of sound in its material and cultural forms. The book considers sounds and music as experienced in such diverse settings as shop floors, laboratories, clinics, design studios, homes, and clubs, across an impressively broad range of historical periods and national and cultural contexts.
Science has traditionally been understood as a visual matter, a study which has historically been undertaken with optical technologies such as slides, graphs, and telescopes. This book questions that notion powerfully by showing how listening has contributed to scientific practice. Sounds have always been a part of human experience, shaping and transforming the world in which we live in ways that often go unnoticed. Sounds and music, the authors argue, are embedded in the fabric of everyday life, art, commerce, and politics in ways which impact our perception of the world. Through an extraordinarily diverse set of case studies, authors illustrate how sounds — from the sounds of industrialization, to the sounds of automobiles, to sounds in underwater music and hip-hop, to the sounds of nanotechnology — give rise to new forms listening practices. In addition, the book discusses the rise of new public problems such as noise pollution, hearing loss, and the “end” of the amateur musician that stem from the spread and appropriation of new sound- and music-related technologies, analog and digital, in many domains of life.”
Publisher Oxford University Press, 2011
ISBN 0199995818, 9780195388947
624 pages
Reviews: John F. Barber (Leonardo, 2012), Bruce Johnson (Popular Music, 2013), William Cheng (Journal of the American Musicological Society, 2014).
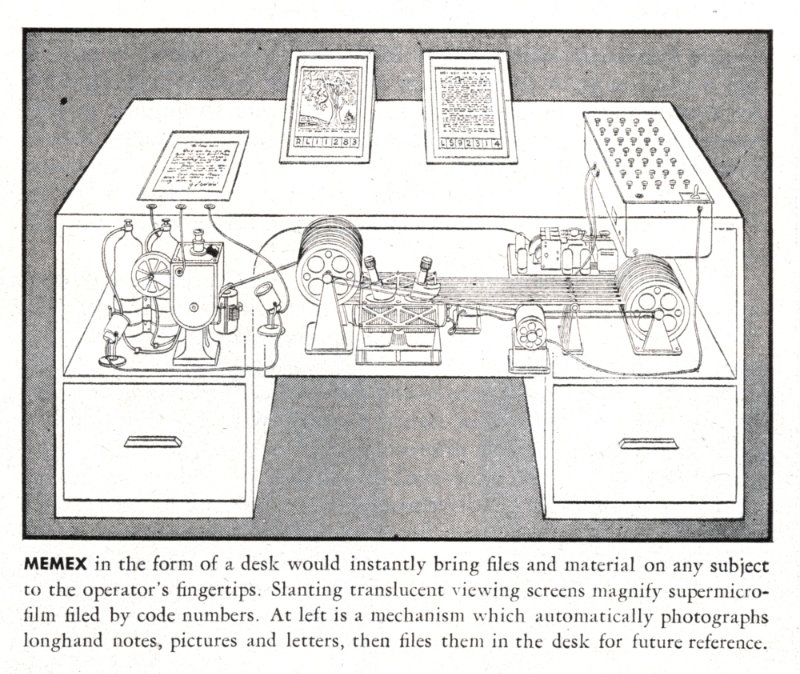
Comment (0)James Nyce, Paul Kahn (eds.): From Memex to Hypertext: Vannevar Bush and the Mind’s Machine (1991)
Filed under book | Tags: · book, computing, history of computing, history of technology, hypertext, reading, technology, writing
“Vannevar Bush, the engineer who designed the world’s most powerful analog computer, envisioned the development of a new kind of computing machine he called Memex. For many computer and information scientists, Bush’s Memex has been the prototype for a machine to help people think.
This volume, which the editors have divided into sections on the creation, extension, and legacy of the Memex, combines seven essays by Bush with eleven others by others that set his ideas within a variety of contexts. The essays by Bush range chronologically from the early “The Inscrutable Thirties” (1933), “Memorandum Regarding Memex” (1941), and “As We May Think” (1945), to “Memex II” (1959), “Science Pauses” (1967), “Memex Revisited” (1967), and a passage from “Of Inventions and Inventors” (1970). Bush’s essays are surrounded by four chapters that place his changing plans for the Memex within his career and within information technology before digital computing.”
Contributors include Larry Owens, Colin Burke, Douglas C. Engelbart, Theodor H. Nelson, Linda C. Smith, Norman Meyrowitz, Tim Oren, Gregory Crane, and Randall H. Trigg.
Publisher Academic Press, San Diego and London, 1991
ISBN 0125232705, 9780125232708
367 pages
via Marcell Mars, in the Unlimited Edition
Memex animation (1995)
Review (George P. Landow, The Journal of Computing in Higher Education, 1992)
Review (Matthew Wall, College & Research Libraries, 1992)
Review (Liam Murray, ReCALL, 1993)
Almanacco Letterario Bompiani: Elettronica e letteratura (1961) [Italian]
Filed under magazine | Tags: · automation, computing, digital humanities, humanities computing, language, linguistics, literary theory, literature, philology, robots

An early document from the field of humanities computing, today widely known as digital humanities.
Elettronica e letteratura is the title of the thematic section of an annual literary almanac published by Valentino Bompiani since 1925. The section contains the historical excursions by Rinaldo De Benedetti, Michele Pacifico and Franco Lucentini, and the reports on scientific research sponsored by Olivetti and IBM Italy and conducted by Roberto Busa, Stanislao Valsesia, Carlo Tagliavini, Silvio Ceccato, and Nanni Balestrini.
In one of the articles, the Jesuit priest Roberto Busa, often cited as the pioneer of the field, gives an account of his work on Index Thomisticus, a complete lemmatization of the works of Thomas Aquinas, started in the late 1940s (elsewhere: “During the World War II, between 1941 and 1946, I began to look for machines for the automation of the linguistic analysis of written texts. I found them, in 1949, at IBM in New York City.”).
Included is also a survey about the potential use of computers in literary scholarship (including a response from Pier Paolo Pasolini), entitled “Le due culture” [Two Cultures], and an essay by Umberto Eco.
in Almanacco Letterario Bompiani 1962: Le applicazioni dei calcolatori elettronici alle scienze morali e alla letteratura
Edited by Sergio Morando
Publisher Bompiani, Milan, December 1961
pages 87-188 (of 324)
via P–DPA log
Commentary (Adriano Comai, 1985, in Italian)
PDF (62 MB; large portion of the survey missing, 313ff)
See also an online emulator of Tape Mark 1 and Monoskop page on digital humanities.
Comments (2)